Report Overview
Solid State Battery Market Highlights
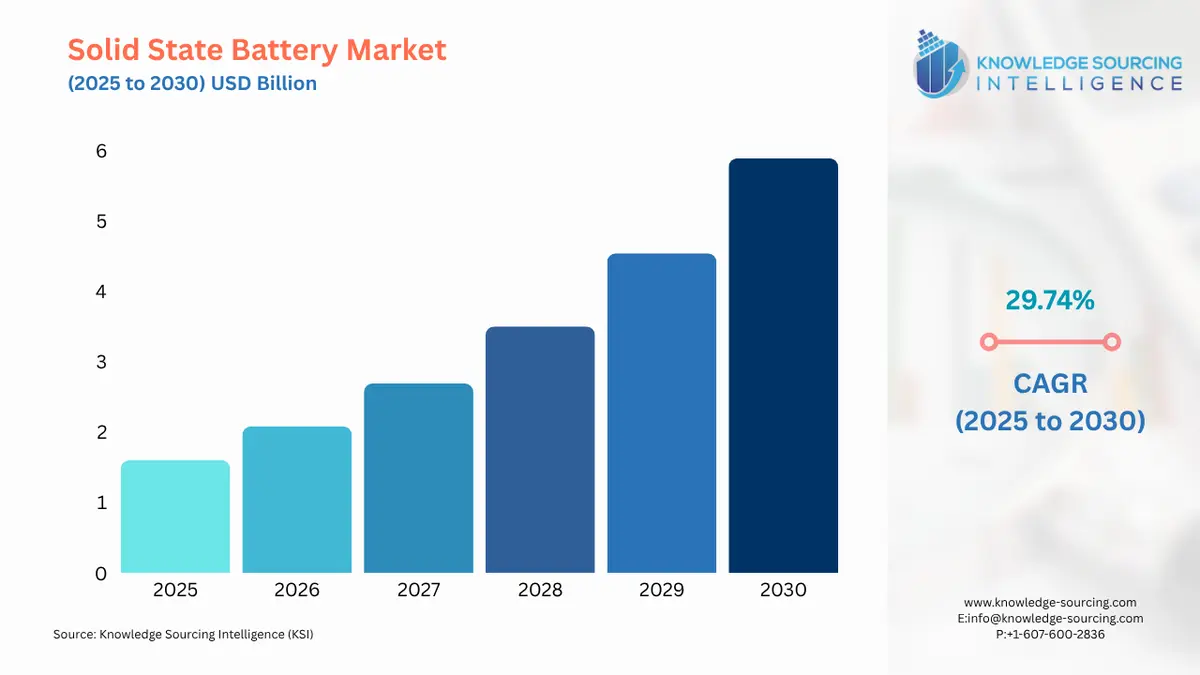
Solid State Battery Market Size:
The Solid State Battery Market is expected to grow from USD 1.601 billion in 2025 to USD 5.886 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 29.74%.
The global energy storage landscape is undergoing a fundamental transformation, with solid-state battery technology emerging as a potential successor to the dominant lithium-ion chemistry. Solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid or gel electrolyte of conventional batteries with a solid counterpart, offer a pathway to address the key limitations of current battery technology. These include the risks of thermal runaway, lower energy density, and extended charging times, which are significant constraints in high-stakes applications such as electric vehicles and aerospace. The market's evolution is not a simple linear progression but a complex ecosystem of technological innovation, strategic corporate investments, and supportive government policies. The demand for solid-state batteries is not a generic trend but is explicitly driven by specific industry needs for performance and safety that traditional batteries cannot meet.
Solid State Battery Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The solid-state batteries market is propelled by a confluence of factors directly related to the performance and safety requirements of end-user industries. The electric vehicle (EV) sector is the most significant growth driver. Automakers are under intense pressure to improve EV range, shorten charging times, and enhance vehicle safety to accelerate consumer adoption. Solid-state batteries address these imperatives by offering a theoretical energy density approximately double that of conventional lithium-ion batteries, which can enable a longer driving range without increasing battery size or weight. The absence of a flammable liquid electrolyte also substantially reduces the risk of battery fire, a key safety concern for consumers. This enhanced safety profile directly increases the attractiveness and, therefore, the demand for vehicles equipped with this technology.
The consumer electronics and wearable devices segments also act as critical growth catalysts. Manufacturers in these sectors seek to produce thinner, lighter devices with extended battery life. Solid-state batteries, with their high energy density and compact form factor, are a compelling solution. The use of a solid electrolyte allows for a thinner battery design, enabling more flexible and innovative device layouts. Furthermore, the IoT and energy harvesting markets require highly reliable, long-life power sources that can operate in a variety of environmental conditions. The inherent stability and durability of solid-state batteries meet these arduous criteria, creating a distinct and growing demand for these specialized products.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The Solid State Battery market faces significant challenges, primarily related to manufacturing complexity and cost. Scaling the production of solid electrolytes and integrating them into a multi-cell battery design is a technically demanding and capital-intensive process. The manufacturing of these batteries requires expensive vacuum deposition equipment and specialized facilities, which create high barriers to entry. This complexity directly impacts market supply, as it limits the ability of companies to ramp up production to meet potential demand, thereby slowing commercialization. Cost remains a major constraint; for instance, historical estimates place the cost of a single 20 Ah solid-state battery cell at a prohibitive price, making it unviable for widespread consumer applications.
Despite these obstacles, the market is rich with opportunities. The imperative to overcome manufacturing hurdles has catalyzed a wave of strategic partnerships. Automakers are collaborating with battery startups to co-develop and scale production, providing the necessary capital and industrial expertise. This collaboration accelerates the time to market and de-risks the commercialization process for both parties. The opportunity also extends to the development of new materials. Advancements in sulfide, oxide, and polymer electrolytes that improve ionic conductivity and stability could unlock performance breakthroughs and reduce manufacturing costs. Companies that can solve these chemistry challenges stand to gain a significant competitive advantage. The focus on safety also creates an opportunity for solid-state batteries to capture a premium market segment where safety is a paramount concern, such as in medical implants and aerospace applications, where demand is less elastic to price.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The Solid State Battery market relies on a complex supply chain of critical raw materials, many of which are also used in conventional lithium-ion batteries, including lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The pricing dynamics of these materials directly influence the final cost of solid-state batteries. Lithium, a key component of both the anode and cathode, is subject to global supply and demand fluctuations. While some long-term agreements between suppliers and end-users have been established to stabilize prices, the market remains volatile. The price of battery-grade lithium carbonate, for example, is influenced by mining output, geopolitical factors, and the overall demand from the EV and energy storage sectors.
Solid-state battery chemistry, particularly those using lithium metal anodes, theoretically reduces the need for other expensive materials like cobalt and nickel, which are used in many conventional lithium-ion cathodes. This shift can serve as a long-term pricing advantage. However, the supply chain for solid electrolytes introduces new dependencies. The development of sulfide-based electrolytes requires sulfur, while oxide and polymer electrolytes require their own specific precursor chemicals. The scaling of these new material supply chains and the establishment of stable pricing for them is an ongoing challenge. The high cost of specialized manufacturing equipment also adds a significant fixed cost component, which can only be mitigated through large-scale production and economies of scale.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The solid-state battery supply chain is evolving, with key production hubs emerging in Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe. Unlike the well-established lithium-ion supply chain, which is largely centered in Asia, the solid-state battery supply chain is a nascent network characterized by intense R&D and pilot production. The chain begins with the sourcing and refining of raw materials, including lithium, and the specialized materials required for solid electrolytes, such as sulfides or oxides. This is followed by the manufacturing of the solid-state components, including the solid electrolyte separator and the solid electrodes.
These components are then assembled into battery cells and modules. Logistical complexities arise from the need to handle sensitive, high-purity materials and to maintain a controlled environment throughout the manufacturing process. The supply chain for solid-state batteries is not yet fully integrated, with many companies relying on a mix of in-house R&D, pilot production, and strategic partnerships with external suppliers. This creates dependencies and potential bottlenecks, particularly in the production of the solid electrolyte, which is a key technical and financial hurdle. The long-term viability of the market depends on the successful establishment of a scalable, resilient, and cost-effective supply chain that can support mass production.
Solid State Battery Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
European Union |
EU Battery Regulation (Regulation EU 2023/1542) |
This regulation sets comprehensive standards for battery sustainability, safety, and performance. By establishing eco-design requirements, carbon footprint rules, and mandatory recycling targets for batteries, it creates a market imperative for companies to innovate. This directly benefits solid-state battery developers, whose technology inherently offers enhanced safety and the potential for a more sustainable life cycle, thereby making them a more attractive option for compliance. |
|
United States |
U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) - Bipartisan Infrastructure Law |
The DOE's funding and grant programs, such as those established under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, provide substantial capital for battery R&D, manufacturing, and raw material processing. This government support directly subsidizes the high capital expenditures required for pilot production facilities and research, thereby reducing financial risk for companies like Solid Power and accelerating their ability to scale and meet future market trends. |
|
Japan |
Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) - Economic Security Promotion Act |
Japan's government has designated batteries as a critical material and is actively supporting the development and production of next-generation technologies like solid-state batteries. The METI provides certification and financial support for company production plans, as seen with Toyota. This direct government intervention provides a stable regulatory and financial environment for domestic companies, encouraging them to invest heavily in R&D and manufacturing to secure a leadership position in the global market. |
Solid State Battery Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Electric Vehicles
The electric vehicle (EV) segment represents the most significant and immediate growth driver for solid-state batteries. The market's growth hinges on the ability of this technology to address the primary barriers to EV adoption: range anxiety, charging time, and safety. Solid-state batteries, by replacing the traditional liquid electrolyte with a solid one, offer a pathway to higher energy density, which directly translates to a longer driving range for a given battery pack size. This technological advancement directly increases the value proposition of EVs for consumers and commercial fleets. Furthermore, the ability of solid-state batteries to charge from 10% to 80% state of charge in a fraction of the time of their liquid-based counterparts makes EVs as convenient for long-distance travel as internal combustion engine vehicles. The enhanced safety profile, which mitigates the risk of thermal runaway, is a critical factor for consumer confidence and regulatory approval. Automakers are making strategic commitments to this technology, and their investments in co-development and pilot production facilities are a direct reflection of the anticipated demand for solid-state battery-powered vehicles.
- By Type: Lithium-ion Batteries
By type, the solid state battery market is segmented into Lithium-ion batteries, Nickel-Cadmium batteries, Lead-acid batteries, and Others. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are a major component in the electrification of automotive powertrains. They balance energy density, efficiency, and cost. In 2024, the total demand for batteries in electric vehicles (EVs) was over 750 gigawatt-hours (GWh) globally, a 40% increase from the previous year. This increase is the result of growing reliance on Li-ion technology to satisfy the energy storage requirements of the current generation of EVs.
One significant improvement to the Li-ion battery technology has been the falling cost of the batteries per kilowatt-hour (kWh). In 2024, the average price of a lithium-ion battery pack was $115 kWh, the largest decrease per year since 2017. This pricing movement is reflective of many factors, including economies of scale, more manufacturing capacity, and, importantly, switching to the use of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) chemistries that are not reliant on expensive sources of nickel and cobalt.
An important factor in the evolving dynamics of Li-ion battery development in EVs is the increased manufacturing capacity. At the end of 2024, there was a pipeline of over 1,100 GWh of battery cell manufacturing capacity developed in North America. This is part of a greater strategy to localize the manufacturing and development of supply sources to improve energy independence, reduce reliance on foreign supply chains, enhance energy resiliency, and maintain domestic EV demand. Notwithstanding these successes, ongoing challenges remain, particularly with respect to the supply of raw materials.
In conclusion, Li-ion batteries remain an integral part of the EV sector, showing improvements in cost reductions, manufacturing capability, and energy density. However, it will be essential to overcome the supply chain restrictions to ensure that growth is sustained and that the demands of the electric vehicle market are met in the future.
The growth in registrations of electric vehicles leads to an increase in demand for lithium-ion batteries, as these batteries are the main source of energy for almost all EVs. The increase in registered electric vehicles leads to a proportional increase in both the manufacture and installation of Li-ion battery packs. This growth in the number of vehicles requires a corresponding increase in battery manufacturing to meet the growing energy storage requirements. This is paralleled by an increased importance of growth in battery performance, energy density, and safety. Following registrations of electric vehicles is an excellent measurable quantity of market expansion for Li-ion batteries linked to indices of consumer uptake trends and the technological and industrial growth in the energy storage sector.
- By End-User Industry: Consumer Electronics
The consumer electronics industry, encompassing smartphones, laptops, and a variety of smaller gadgets, is a key early adopter and demand driver for solid-state batteries. This sector’s growth is driven by the constant consumer desire for thinner, lighter devices with longer battery life. Solid-state batteries provide a solution by enabling higher energy density in a more compact form factor. This ensures a significant increase in a device's runtime without a proportional increase in its physical size. Wearable devices, in particular, benefit from the technology's flexible form factor and enhanced safety. The solid electrolyte's non-flammable nature is a critical selling point for products worn on the body. The necessity for solid-state batteries in this sector is also influenced by the need for more robust and durable power sources that can withstand repeated charge cycles and mechanical stress. The ability of solid-state batteries to operate reliably and safely in these high-cycle applications directly propels demand within the consumer electronics and wearable segments.
Solid State Battery Market Geographical Analysis:
- US Market Analysis
The US market for solid-state batteries is characterized by a strong focus on innovation and a strategic push to build a domestic battery supply chain. The market is primarily driven by the automotive industry, which is actively investing in technology to compete in the global EV market. The U.S. government, through agencies like the Department of Energy, is a major catalyst, providing significant grants and funding to accelerate R&D and build out manufacturing capacity. This has created a robust ecosystem of startups and established companies working to commercialize the technology. The market is also heavily influenced by partnerships between domestic battery developers and large automotive OEMs. The US regulatory environment, while not as prescriptive as the EU's, supports the market through incentives for EV adoption and investments in clean energy infrastructure, which collectively increase the demand for advanced battery technologies.
- Brazil Market Analysis
The solid-state battery market in Brazil is in a nascent stage, primarily influenced by the broader adoption of electric vehicles and a growing interest in renewable energy storage. Brazil's abundant natural resources, particularly its large lithium deposits, provide a potential long-term advantage in the raw material supply chain. However, the market currently lacks a mature, integrated manufacturing ecosystem for advanced batteries. The solid-state batteries market is driven by a need for more efficient and safer solutions in commercial vehicles and public transportation, as well as in niche industrial applications. The market's future growth depends on the country's ability to attract foreign investment, develop local expertise, and establish supportive government policies to build out a domestic manufacturing base.
- Germany Market Analysis
Germany is a key hub for solid-state battery research and development, driven by its legacy of automotive engineering and its strategic commitment to becoming a leader in battery technology. The market is centered on high-performance batteries for premium vehicles and specialized industrial applications. The German government, through initiatives like the European Battery Alliance, is a significant enabler, providing financial support and a clear regulatory framework to foster innovation. The market's trend is shifting towards high-quality, sustainable batteries that can meet strict performance and safety standards. German companies are actively partnering with battery startups to secure access to technology, and their focus on integrating solid-state batteries into production lines reflects a clear demand for superior battery performance.
- Saudi Arabia Market Analysis
The solid-state battery market in Saudi Arabia is largely driven by the country's long-term economic diversification strategy. The government's Vision 2030 program aims to reduce reliance on oil and gas by investing in new industries, including electric vehicles and renewable energy. This has created a direct demand for advanced energy storage technologies. Saudi Arabia's access to low-cost raw materials and its strategic location make it a potential hub for battery production. The market's growth is dependent on significant foreign investment and technological partnerships to build the necessary manufacturing infrastructure. The need for solid-state batteries in this region is also influenced by large-scale renewable energy projects and the need for high-performance, durable batteries in demanding climatic conditions.
- Japan Market Analysis
Japan is a global pioneer in solid-state battery technology, with a rich history of innovation in materials science. The country's market for solid-state batteries is driven by its leading automotive and consumer electronics industries. Japanese companies, most notably Toyota, are making substantial investments in R&D and pilot production. The government, through the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), is providing a clear framework and financial support to accelerate the commercialization of this technology, ensuring that Japan remains a leader in the global battery race. The demand is not just for technology but for a complete ecosystem, including the development of next-generation materials and manufacturing processes. The Japanese market’s focus on safety, reliability, and long-term performance makes solid-state batteries a natural progression for its core industries.
Solid State Battery Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape of the Solid State Battery market is defined by a dynamic interplay between a small number of well-funded, publicly-traded startups and large, multinational corporations. The competition is not based on market share in a commercial sense, as the technology is not yet mass-produced, but on technological breakthroughs, strategic partnerships, and the ability to scale. Companies are racing to be the first to commercialize a viable product, with success measured by key performance metrics such as energy density, charging speed, and cycle life.
- Solid Power, Inc.: Solid Power's strategic positioning is based on its development of sulfide-based solid electrolytes for all-solid-state batteries. The company operates on a business model of licensing its technology and supplying electrolyte materials to its automotive partners, rather than manufacturing end-use batteries itself. Its partnerships with major automakers like the BMW Group demonstrate its commercialization strategy. This approach reduces the capital burden of building massive gigafactories and focuses on its core intellectual property. Solid Power's recent milestone of delivering A-sample solid-state cells to its automotive partners is a key indicator of its progress towards mass production.
- QuantumScape Corporation: QuantumScape has a differentiated approach focused on developing a solid-state lithium-metal battery with an anode-free cell design. The company's competitive advantage lies in its separator technology, which it produces using a proprietary manufacturing process. QuantumScape's strategic relationship with the Volkswagen Group is a cornerstone of its business model. The company's recent achievement of shipping its first 24-layer prototype cells to automotive OEMs marks a significant step forward in validating its technology's scalability and performance. This milestone is a critical signal of its progress toward commercialization.
- Toyota Motor Corporation: Toyota's competitive strategy is rooted in its extensive R&D capabilities and its long-standing expertise in battery technology. The company has a vast intellectual property portfolio in solid-state batteries and is investing heavily in a vertically integrated supply chain. Toyota's approach is to develop the technology in-house and then scale production with key partners. The Japanese government's certification of Toyota's production and R&D plans for next-generation batteries underscores its leadership position and the national strategic importance of the company's efforts. Toyota's plan to produce all-solid-state batteries for its EVs by the late 2020s positions it as a major, long-term player in the market.
Solid State Battery Market Recent Developments:
- September 2025: QuantumScape Corporation and PowerCo SE, the battery company of the Volkswagen Group, unveiled a Ducati motorcycle powered by QuantumScape's solid-state lithium-metal batteries. The demonstration, which took place at IAA Mobility, showcased the QSE-5 battery cells and highlighted the technology's application in a real-world vehicle. The demonstration follows a series of company milestones, including the integration of its proprietary Cobra separator manufacturing process into baseline production in June 2025.
- May 2025: The BMW Group and Solid Power, Inc. announced that they are testing all-solid-state battery cells in a BMW i7 vehicle. This joint development and testing agreement is a critical step in the ongoing collaboration between the two companies. It demonstrates a direct progression from laboratory-based research to the testing of a functional battery in a real-world vehicle, providing a clear pathway toward a potential commercial product.
- January 2024: Solid Power, Inc. licensed its cell designs and production processes to SK On and will install a pilot cell production line at SK On's facility in Korea. The agreement also includes a commitment to supply SK On with sulfide-based solid electrolyte materials. This development expands Solid Power's strategic influence by directly supporting the scale-up of its technology by a major battery manufacturer in a key region.
Solid State Battery Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 1.601 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 5.886 billion |
| Growth Rate | 29.74% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Type, Application, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Solid State Battery Market Segmentation:
- By Type
- Lithium-ion batteries
- Nickel-Cadmium batteries
- Lead-acid batteries
- Others
- By Application
- Consumer Electronics
- Electric Vehicles
- Medical Devices
- Wearable Devices
- IoT / Energy Harvesting Devices
- Aerospace & Defense
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- South America
- Europe
- Middle East and Africa
- Asia Pacific