Report Overview
Global Medical Tubing Market Highlights
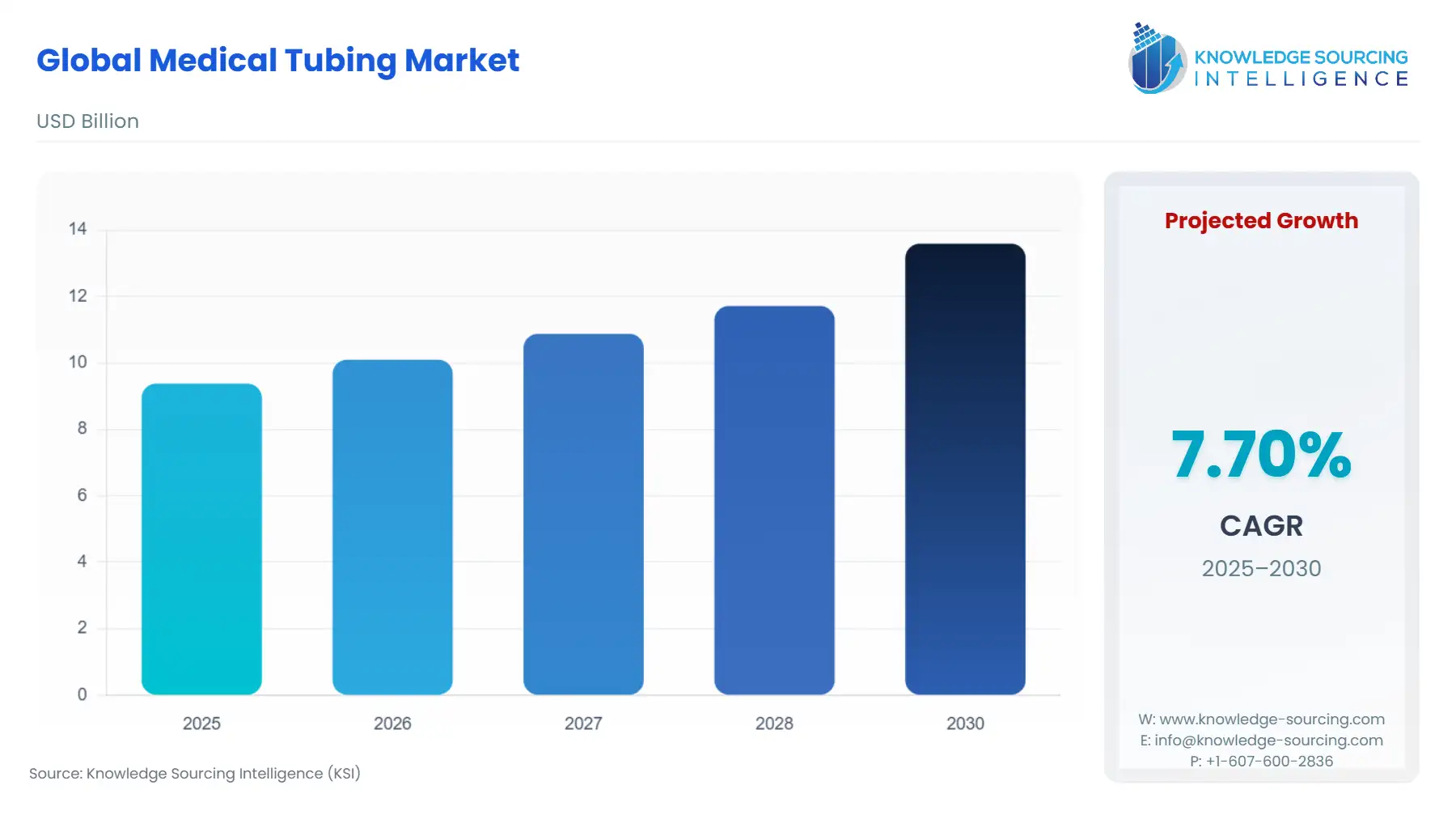
Medical Tubing Market Size:
The Global Medical Tubing Market is expected to grow from USD 9.379 billion in 2025 to USD 13.593 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 7.70%.
The Global Medical Tubing Market, a foundational component of the broader medical device industry, is undergoing a transformation shaped by clinical necessity and regulatory mandates. Medical tubing serves a non-negotiable role in fluid management, drug delivery, and device function across nearly all healthcare settings, from operating theaters to home-care environments. Its growth trajectory is inextricably linked to the rising burden of chronic and age-related diseases, which compel the healthcare system to adopt more efficient and patient-friendly treatment modalities. . The criticality of tubing in procedures like continuous drug infusion, dialysis, and catheterization cements its essential status within the medical value chain.
Global Medical Tubing Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The increasing global prevalence of chronic illnesses, such as cardiovascular and urological disorders, acts as the primary catalyst, directly accelerating the demand for associated interventional devices. These conditions necessitate constant monitoring, drug delivery, and diagnostic procedures, fundamentally driving the consumption of bulk disposable tubing, intravenous (IV) lines, and specialty catheter tubing.
Furthermore, the persistent clinical shift toward minimally invasive procedures—preferred for their reduced patient recovery times and lower complication rates—creates a direct, inelastic demand for advanced, precision-engineered tubing. Specifically, these procedures require specialized products, including co-extruded and multi-lumen tubing, designed for high flexibility, kink resistance, and safe navigation within the body.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A principal challenge facing the market is the increasing stringency of global medical device regulations, notably the EU’s MDR, which escalates the cost and time required for product development and certification. This regulatory environment creates a substantial barrier to entry and forces manufacturers to invest heavily in verifying the biocompatibility and material consistency of their tubing, ultimately raising production costs and potentially restraining demand from price-sensitive end-users. Conversely, this regulatory pressure generates a significant opportunity: the mandate to eliminate controversial plasticizers, such as phthalates from PVC, is fueling an innovative demand wave for next-generation, non-phthalate plasticized PVC compounds and alternative materials like TPE and TPU. This material substitution trend opens profitable avenues for companies capable of supplying high-grade, certified, compliant polymer solutions.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The medical tubing market, being a physical product industry, is heavily reliant on the supply and stable pricing of key raw materials, predominantly silicone polymers, Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and various Polyolefin and Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs). Medical-grade silicone, favored for its superior biocompatibility, flexibility, and thermal stability, commands a higher cost structure compared to PVC. The cost of manufacturing silicone tubing is inherently high due to precision molding, advanced sterilization, and rigorous quality control protocols, factors that contribute to higher product prices and limit adoption in cost-sensitive markets. PVC, while offering a cost-effective alternative and dominating the disposable tubing segment, is subject to material constraints driven by the transition away from traditional phthalate plasticizers. This mandatory substitution for materials like DOTP introduces supply chain adjustments and pricing volatility in the short term, as manufacturers adapt to and scale production of these new compliant compounds.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global medical tubing supply chain is characterized by a high degree of specialization and a critical dependence on a limited number of specialized polymer and compound suppliers. Key production hubs are concentrated in North America and Europe, aligning with major medical device manufacturing clusters, though Asia-Pacific is rapidly expanding its production capacity. A significant logistical complexity is the need to maintain ISO Class 8 cleanroom standards throughout the final extrusion and assembly processes, which limits the number of qualified manufacturing sites. This structure results in a dependency on long-distance logistics for raw polymer resins, making the chain vulnerable to geopolitical and trade-related disruptions. The imposition of tariffs on specialized polymer imports or manufactured components, while not creating a new segment, introduces a specific cost headwind that is ultimately passed down to device manufacturers, potentially slowing the adoption rate of certain high-cost, specialized tubing in affected markets due to increased procurement expenses.
Medical Tubing Market Government Regulations
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
European Union |
Medical Device Regulation (MDR) (Regulation (EU) 2017/745) |
The MDR imposes stricter requirements on clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and material composition. This regulation directly increases the demand for high-end, traceable, and highly biocompatible materials and elevates the administrative and cost burden for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs), pushing out non-compliant products and constraining supply. |
|
United States |
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Quality System Regulation (QSR) (21 CFR Part 820) |
The QSR mandates comprehensive quality management systems for medical device manufacturing, including material selection and control. This drives a consistent, high-demand baseline for manufacturers capable of producing defect-free, batch-to-batch consistent tubing. It also indirectly increases demand for automated, in-line quality control systems to ensure compliance with strict dimensional and material specifications. |
|
India |
Medical Devices Rules, 2017 (MDR 2017) |
As India works to develop a robust domestic MedTech market and attract foreign investment, its evolving regulations introduce both compliance complexity and opportunity. The government's Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme aims to bolster domestic manufacturing capacity, potentially increasing future local demand for raw materials and component tubing as companies seek to qualify for subsidies, while initially complex regulations may slow market entry for foreign manufacturers. |
Global Medical Tubing Market In-Depth Segment Analysis
- By Application: Catheters
The Catheters segment represents a primary driver of high-value demand within the medical tubing market, fundamentally shifting the focus from simple fluid transfer to complex mechanical functionality. Catheters are essential for critical minimally invasive procedures across cardiology, urology, and neurovascular intervention. The demand driver here is the rising global incidence of chronic diseases, particularly cardiovascular conditions. Each complex procedure, such as cardiac catheterization or angioplasty, requires sophisticated tubing that functions as the device’s structural backbone. This creates acute demand for multi-lumen tubing, which allows for simultaneous drug infusion, guide-wire movement, and pressure monitoring through separate channels. It also fuels demand for braided tubing or other reinforced structures, necessary to provide torque, steerability, and pressure resistance for navigating intricate vasculature. The demand is not merely volume-based but centers on advanced extrusion capabilities, directly correlating to improved clinical outcomes.
- By Material: Silicone Polymers
The Silicone Polymers segment is characterized by a premium demand profile, driven almost exclusively by the imperative for advanced biocompatibility and performance in long-term or high-risk applications. Silicone tubing possesses a natural chemical inertness and excellent thermal stability, making it the preferred material for applications involving prolonged contact with biological fluids or human tissue, such as peristaltic pump tubing, chronic drainage systems, and respiratory apparatus. The key demand driver is the escalating requirement for enhanced patient safety and reduced risk of Hospital-Acquired Infections (HAIs). Silicone's ability to be sterilized via various methods without significant degradation makes it indispensable. Furthermore, its superior flexibility and durability support demand in complex, dynamic-stress applications, which require tubing that can withstand constant compression and flow without leaching or particulate shedding. The demand for silicone is therefore a direct function of stringent safety protocols and mechanical performance requirements.
Global Medical Tubing Market Geographical Analysis
- US Market Analysis (North America)
The US market commands a dominant position, driven by a high rate of technological adoption, substantial R&D expenditure, and a well-established infrastructure for advanced medical procedures. Local demand is heavily concentrated on sophisticated, high-margin products like micro-extruded and multi-lumen tubing for neurovascular and cardiovascular devices. The key local demand factor is the high per capita incidence of chronic disease, coupled with a fee-for-service healthcare model that favors innovative, complex interventional procedures.
Furthermore, compliance with the stringent FDA Quality System Regulation (QSR) maintains a high barrier to entry for foreign suppliers, driving domestic manufacturers to focus on validated, high-quality material formulations and precision manufacturing, which directly translates to strong, consistent demand for premium tubing.
- Brazil Market Analysis (South America)
Brazil represents the largest and most dynamic market in South America, where demand is primarily influenced by an expanding public and private healthcare infrastructure and a growing patient population. The main local factor driving demand is the need for cost-effective, high-volume products, particularly bulk disposable tubing and standard IV sets utilizing PVC. While a growing middle class is increasing demand for advanced procedures, market growth is often constrained by economic volatility and public-sector budgeting limitations. This creates a polarized demand environment: a niche market for high-end catheter tubing for specialized clinics, alongside a dominant, price-sensitive requirement for essential, low-cost tubing to support routine hospital and clinic operations.
- Germany Market Analysis (Europe)
Germany is a European anchor market, characterized by mature healthcare spending and a robust medical device manufacturing sector. Demand is critically driven by the necessity for compliance with the new European Medical Device Regulation (MDR). This regulation significantly pressures manufacturers to adopt non-phthalate and highly biocompatible materials for all medical tubing, creating an immediate, non-negotiable demand for high-performance TPE, TPU, and advanced silicone compounds. German manufacturers, focused on exporting high-quality, high-reliability devices, prioritize tubing that provides exceptional material traceability and validation, reinforcing demand for premium, certified European-sourced products.
- Saudi Arabia Market Analysis (Middle East & Africa)
The Saudi Arabian market is experiencing accelerated demand, primarily fueled by significant government investments in modernizing and expanding healthcare infrastructure under the Vision 2030 program. This national strategic investment is the key local demand driver, leading to the construction of new specialized hospitals and medical cities. This expansion generates a massive, immediate demand for a full spectrum of medical consumables, including all categories of tubing for new dialysis centers, operating rooms, and long-term care facilities. The demand profile is highly dependent on imports, placing a premium on resilient, high-volume supply chains capable of navigating regional logistics and local regulatory clearance for imported devices.
- China Market Analysis (Asia-Pacific)
China's medical tubing market is fueled by an enormous and rapidly aging patient population and a sustained, aggressive government push for domestic device manufacturing and self-sufficiency. The primary local demand factor is the sheer scale of chronic disease burden, particularly in cardiovascular and diabetes care, which requires mass production of disposable and bulk tubing for routine procedures. Government policies and investment programs, such as "Made in China 2025," are simultaneously stimulating demand for high-precision, domestically-produced components. This results in a dual-market dynamic: ongoing, large-scale demand for cost-competitive commodity tubing, coupled with rapidly emerging, high-growth demand for advanced, multi-functional tubing to support the nation's indigenous development of complex catheter and drug delivery systems.
Global Medical Tubing Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The global medical tubing market is characterized by medium concentration, with a competitive landscape featuring large, diversified polymer and materials science corporations alongside highly specialized, precision extrusion firms. The primary axis of competition has shifted from basic material cost to specialized technical capabilities, particularly multi-lumen extrusion, material compounding expertise (e.g., non-phthalate plasticizers), and ISO-certified cleanroom manufacturing scale. Major players leverage their global footprint and deep material science heritage to serve Tier 1 medical device manufacturers, while niche specialists compete on micro-extrusion precision and custom polymer formulation for highly specialized therapeutic applications.
- Saint-Gobain- Saint-Gobain is strategically positioned as a diversified materials science powerhouse, with its medical tubing operations focusing on high-performance polymer solutions under its Life Sciences sector. Their key products, such as those used in peristaltic pumping, cater to the bioprocessing industry, aligning their growth with the surging global demand for biologics and advanced therapies, which require uncompromising tubing quality for sterile and precise fluid handling. Their strategic positioning leverages a deep heritage in material expertise, allowing them to provide a wide array of specialized tubing, particularly those made from silicone, TPE, and high-performance fluoropolymers, which are critical for biopharmaceutical fluid transfer and demanding medical device applications.
- Freudenberg Medical- Freudenberg Medical, a subsidiary of the global technology group Freudenberg, is strategically positioned as a dedicated contract manufacturing and components partner to the medical device industry. Their core offering lies in precision extrusion and molding, with a strong focus on advanced silicone, thermoplastic, and composite tubing. Their competitive advantage stems from end-to-end service capabilities, including custom compounding, micro-extrusion, and sub-assembly, which address the complex design and functional needs of minimally invasive devices.
Global Medical Tubing Market Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Junkosha announced a new Clear Peelable FEP-based Heat-Shrink Tubing targeted at catheter assembly, which the company showcased at Medical Technology Ireland 2025. The product delivers exceptional optical clarity and is designed to be peelable so manufacturers can eliminate the traditional skiving step — reducing assembly time, improving yields, and making inspection and handling more ergonomic.
- In April 2025, DuPont introduced Liveo Pharma TPE Ultra-Low Temp Tubing, a sterilizable, weldable, and sealable thermoplastic-elastomer tubing made in an ISO Class-7 cleanroom and aimed at single-use and fluid-transport bioprocessing.
Global Medical Tubing Market Segmentation
- By Material
- Polyvinyl Chloride
- Polyethylene
- Polypropylene
- Silicone Polymers
- Bioabsorbable Polymers
- Others
- By Structure
- Single Lumen
- Multiple Lumen
- Co-Extruded
- Tapered/ Bump Tubing
- Braided Tubing
- Balloon Tubing
- Heat Shrink Tubing
- By Application
- Drug Delivery
- Dialysis
- Intravenous (IV)
- Catheters
- Feeding Tubes
- Biopharma lab equipment
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- UK
- Germany
- France
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- UAE
- Israel
- Saudi Arabia
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- India
- Australia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Taiwan
- Others
- North America