Report Overview
Biopesticides Market Report, Size, Highlights
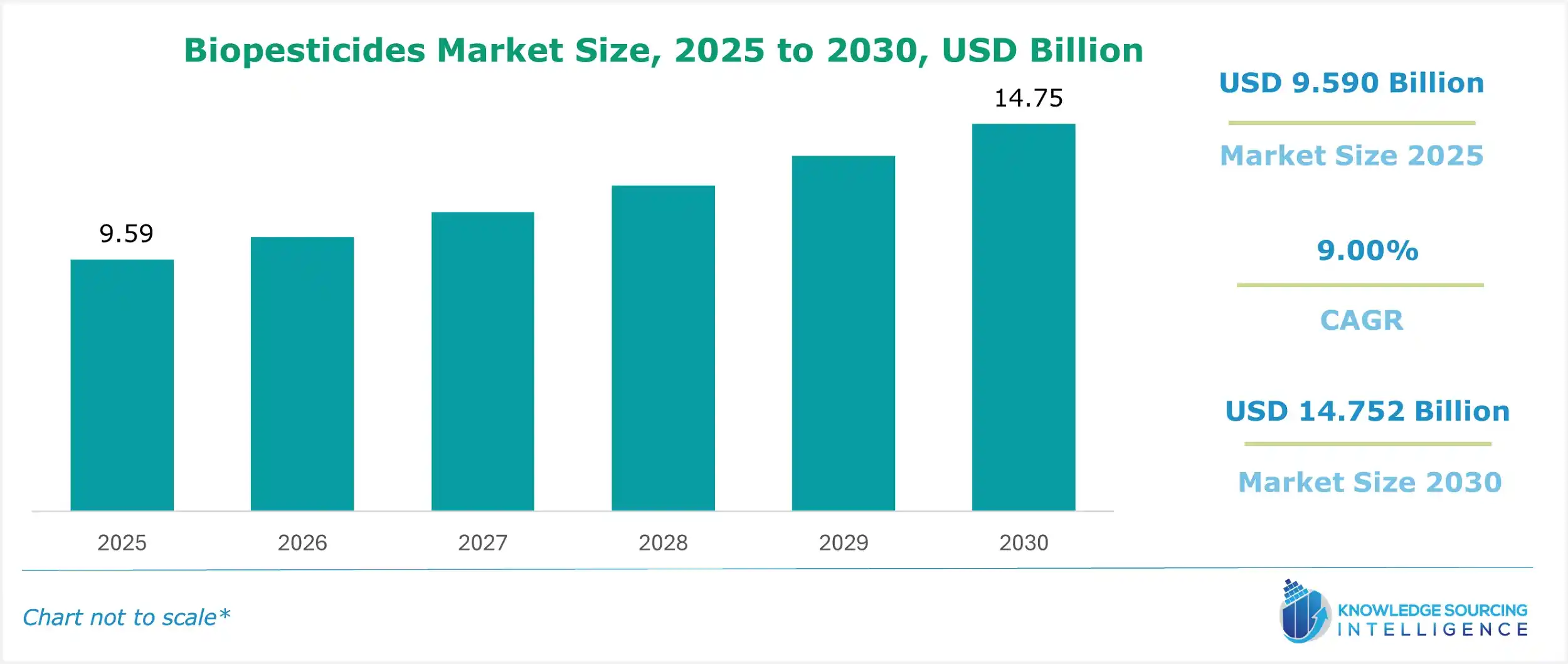
Biopesticides Market Size:
The Biopesticides Market is expected to grow from USD 9.590 billion in 2025 to USD 14.752 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 9.00%.
Introduction to the Biopesticide Market:
The biopesticide market has emerged as a critical segment within the broader agricultural industry, reflecting a global shift toward sustainable and environmentally responsible pest management solutions. Biopesticides, derived from natural sources such as microorganisms, plants, animals, or minerals, offer an alternative to synthetic chemical pesticides, addressing growing concerns about environmental impact, food safety, and regulatory pressures. These products include microbial pesticides, such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses, biochemical pesticides, like plant extracts and pheromones, and beneficial organisms, like predatory insects. As agriculture faces the dual challenge of increasing food production to meet a projected global population of 9.7 billion by 2050 while minimizing ecological harm, biopesticides are gaining traction for their ability to target pests with reduced risks to non-target organisms, human health, and ecosystems.
The biopesticide market is rapidly advancing, driven by demand for biological crop protection and sustainable pest management. Eco-friendly pesticides, derived from natural sources like microbes, plants, or biochemicals, offer effective alternatives to synthetic chemicals, aligning with green agriculture solutions. The agri-biologicals sector is expanding as farmers prioritize environmentally safe practices to meet regulatory standards and consumer preferences. Biopesticides enhance crop resilience while minimizing ecological impact, supporting biodiversity and soil health. With innovations in formulation and delivery, this sector is poised for growth, addressing global challenges in food security and sustainable agriculture for industry stakeholders.
The market is also growing significantly due to increased consumer demand for organic and sustainably produced food, advancements in biotechnology, and stricter regulations on synthetic pesticides. The market expansion is especially notable in regions such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, where there is an increasing adoption of organic farming and integrated pest management (IPM) practices. This expansion is supported by innovations in biopesticide formulations, enhanced efficacy, and a rising number of farmers aiming to meet environmental standards and consumer preferences.
The biopesticide market has seen notable advancements in 2024 and early 2025, reflecting its dynamic nature. For instance, companies are increasingly focusing on biofungicides and bionematicides to address soil-borne diseases and pests, with products like Trichoderma-based formulations gaining popularity. A 2024 Journal of Applied Microbiology study demonstrated Trichoderma’s efficacy against fungal pathogens in crops like tomatoes and maize. The integration of biopesticides into Integrated Pest Management (IPM) systems is growing, as farmers increasingly combine biological controls with cultural and mechanical practices to improve crop protection. The OECD’s 2025 Expert Group on Biopesticides Seminar highlighted the importance of formulating problems within regulatory frameworks to expedite the market entry of new biopesticide products.
A significant development is the emergence of digital agriculture tools, including geospatial data platforms that facilitate the precise application of biopesticides. The FAO's 2024 report on agroecological innovations emphasizes that real-time data enhances the effectiveness of biopesticides by optimizing the timing and targeting of applications. Furthermore, collaborations between academia, industry, and governments are accelerating biopesticide innovation. For example, the University of California, Riverside, partnered with a biotech firm to develop RNAi-based biopesticides targeting citrus pests in 2025.
Biopesticides Market Trends:
The biopesticide market is evolving rapidly, driven by the rising demand for organic food and pesticide residue reduction. Sustainable farming practices are gaining traction, with biopesticides supporting climate-resilient agriculture by offering eco-friendly alternatives to chemical pesticides. Integrated pest management (IPM) adoption is increasing, leveraging biopesticides for effective pest resistance management, reducing reliance on synthetic inputs. Innovations in microbial and biochemical formulations enhance efficacy, aligning with regulatory pressures and consumer preferences for safer, environmentally friendly solutions. As global agriculture embraces sustainability, biopesticides are critical for balancing productivity and ecological health, shaping the future of pest management.
Biopesticides Market Growth Drivers:
- Growing Demand for Organic and Sustainable Agriculture: The global organic food market is growing rapidly due to increased consumer awareness of health, environmental, and ethical concerns. Biopesticides play a crucial role in organic farming, as they comply with certification standards that prohibit synthetic chemicals. For instance, the Research Institute of Organic Agriculture (FiBL) reported that global organic farmland grew to 76 million hectares in 2023, a trend that continues to drive biopesticide adoption. This growth is particularly strong in Europe and North America, where organic food sales are projected to continue rising in 2025. For example, the Organic Trade Association noted a 7.7% increase in U.S. organic food sales in 2024, reaching $69.7 billion. Biopesticides, including neem-based formulations and microbial agents such as Bacillus subtilis, are essential for complying with organic standards while effectively managing pests. This drives farmers to adopt these solutions in pursuit of premium market prices for their organic produce.
- Stringent Regulatory Frameworks: Governments worldwide are imposing stricter regulations on synthetic pesticides due to their environmental and health impacts. The European Union’s Farm to Fork Strategy, part of the European Green Deal, aims to reduce chemical pesticide use by 50% by 2030, creating a favorable environment for biopesticides. This policy has accelerated biopesticide adoption in Europe, where products like Beauveria bassiana-based insecticides are gaining traction. Similarly, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has streamlined registration processes for biopesticides, recognizing their lower toxicity and environmental impact compared to synthetic alternatives. The EPA’s Biopesticide and Pollution Prevention Division reported a 15% increase in biopesticide registrations in 2024, facilitating faster market entry. In Asia, countries like India are promoting biopesticides through initiatives like the National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture, which incentivizes eco-friendly pest management. These regulatory shifts are compelling farmers to adopt biopesticides to comply with legal requirements and maintain market access.
- Advancements in Biotechnology: Innovations in microbial and biochemical technologies are enhancing the efficacy and scalability of biopesticides. For example, the development of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)-based products and RNA interference (RNAi) technologies has improved pest specificity and reduced application frequency. Recent studies, such as those published in the journal Nature Biotechnology (2024), highlight RNAi’s potential to target pests without harming beneficial species. Companies are also developing novel formulations, such as encapsulated biopesticides, to improve stability and application efficiency. A 2025 report from the International Society for Microbial Ecology noted that advancements in metagenomics are enabling the discovery of new microbial agents for biopesticide development, expanding the market’s product pipeline. These technological breakthroughs are reducing application costs and increasing farmer confidence in biopesticides, driving market growth.
- Climate Change and Pest Proliferation: Climate change is exacerbating pest pressures by increasing pest populations and expanding their geographic range, necessitating adaptive pest management solutions. Rising global temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are enabling pests like the fall armyworm and locusts to thrive in new regions, threatening crop yields. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported in its 2025 assessment that climate-driven pest proliferation could reduce global crop yields by up to 20% without effective interventions. Biopesticides, with their targeted mechanisms and lower environmental footprint, are well-suited to address these challenges. For example, pheromone-based biopesticides are being used to disrupt pest mating cycles in regions affected by climate-induced pest surges, as noted in a 2024 Journal of Pest Science study. The ability of biopesticides to integrate into adaptive pest management strategies is driving their adoption in climate-vulnerable regions, particularly in Africa and South Asia.
Biopesticides Market Restraints:
- High Development and Production Costs: The development and production of biopesticides involve significant financial investment, posing a challenge for manufacturers, particularly smaller firms. Unlike synthetic pesticides, which benefit from established production processes and economies of scale, biopesticides often necessitate intricate fermentation, extraction, or formulation techniques. These processes increase costs and limit scalability, especially for microbial biopesticides like those based on Trichoderma or Pseudomonas. A 2025 study in MDPI’s Agronomy journal noted that production costs for microbial biopesticides can be 20–30% higher than for synthetic alternatives due to specialized equipment and quality control requirements. Moreover, the regulatory approval process is streamlined in some areas, but it remains costly and time-consuming. Small-scale manufacturers often struggle to meet compliance standards. For instance, a 2024 Journal of Cleaner Production article noted that the average cost of registering a new biopesticide in the EU can exceed €1 million, deterring innovation among smaller players. These high costs can result in higher prices for end-users, potentially limiting adoption among cost-sensitive farmers in developing regions.
- Limited Shelf Life and Efficacy: Biopesticides, particularly those based on living organisms or biochemicals, often have shorter shelf lives and require precise application conditions compared to synthetic pesticides. Microbial biopesticides, such as Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) or Beauveria bassiana, are sensitive to environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and UV radiation, which can reduce their effectiveness in field conditions. A 2024 Frontiers in Plant Science study emphasized that improper storage or application timing can decrease the efficacy of microbial biopesticides by up to 40%, making them less reliable for farmers accustomed to the consistent performance of chemical pesticides. For example, biofungicides like Trichoderma harzianum require specific soil moisture levels to colonize effectively, limiting their use in arid regions. This variability in performance can erode farmer confidence, particularly in large-scale conventional farming systems where predictability is critical. Ongoing research into stabilized formulations, such as microencapsulation, aims to address these issues, but widespread commercialization remains limited, as noted in a 2025 Biotechnology Advances review.
- Farmer Awareness and Adoption Barriers: Many farmers, particularly in developing regions, lack knowledge about biopesticides or access to training on their use. Legal frameworks and farm structures also influence adoption rates, as outlined in a 2025 MDPI study on biopesticide adoption models.
Biopesticides Market Segmentation Analysis:
- By Type, the bio-insecticides segment is experiencing significant growth
Bio-insecticides represent the largest segment of the biopesticide market, accounting for approximately 50% of the global market share in 2024 due to their widespread use in controlling insect pests across various crops. These products, derived from microorganisms, such as B.thuringiensis, Beauveria bassiana, plant extracts, like neem oil and pyrethrins, or pheromones, are highly valued for their specificity and reduced environmental impact. The rise of bio-insecticides is fueled by the growing presence of insect pests, such as the fall armyworm and whiteflies, which pose a threat to global crop yields. A 2024 study in the Journal of Pest Science demonstrated that Bt-based bio-insecticides effectively reduce lepidopteran pest damage by 70–90% when incorporated into integrated pest management (IPM) programs.
Recent innovations, such as RNAi technology, are enhancing the performance of bio-insecticides by targeting pest-specific genes, as shown in a 2024 study published in Nature Biotechnology. Additionally, the rise of precision application technologies, such as drone-based spraying, is improving the efficacy of bio-insecticides, particularly for large-scale farming operations, as noted in a 2024 FAO report on agroecological innovations.
- By Crop Type, the Food and Vegetables segment is rising considerably
The food and vegetables segment is the leading crop type for biopesticide application, driven by high consumer demand for organic produce and stringent residue regulations in this category. This segment accounted for over 40% of biopesticide market revenue in 2024, as vegetables like tomatoes, cucumbers, and leafy greens are highly susceptible to pests and diseases, necessitating effective pest management solutions. The FiBL reported that organic vegetable production grew by 5.2% globally in 2023, with biopesticides playing a critical role in meeting organic certification standards. Biofungicides such as Trichoderma harzianum are commonly used to control soil-borne diseases in vegetable crops. A study published in the Journal of Applied Microbiology in 2024 demonstrated a 60% reduction in fungal pathogens in tomato fields. The segment’s growth is also driven by consumer awareness of pesticide residues. A 2025 MDPI study shows that 70% of consumers in developed markets prefer vegetables free from residues, which boosts the adoption of biopesticides, such as neem-based insecticides and sulfur-based fungicides. Additionally, advancements in biopesticide formulations tailored for high-value vegetable crops, such as encapsulated microbial agents, are enhancing efficacy and adoption rates.
Biopesticides Market Geographical Outlook:
- The North American market is experiencing substantial expansion
North America is the largest market for biopesticides, accounting for approximately 35% of global market revenue in 2024. This expansion of organic farming, supportive regulations, and advanced agricultural infrastructure also drives market growth. The United States leads this region, fueled by its substantial organic food market and the increasing adoption of integrated pest management (IPM) practices. According to the Organic Trade Association, U.S. organic food sales reached $69.7 billion in 2024, with biopesticides playing a crucial role in organic pest management. The EPA’s Biopesticide and Pollution Prevention Division has facilitated market growth by approving 15% more biopesticide products in 2024, including bio-insecticides and biofungicides for crops like fruits and vegetables.
Canada and Mexico also contribute significantly, with Canada’s organic sector expanding by 6% in 2023, as reported by FiBL. Recent developments, such as the University of California, Riverside’s 2025 partnership with a biotech firm to develop RNAi-based biopesticides for citrus pests, underscore North America’s role as an innovation hub. The region’s advanced distribution networks and farmer training programs further support biopesticide adoption, particularly for high-value crops. For instance, a 2024 MDPI study highlighted that 80% of U.S. organic farmers use biopesticides in vegetable production, driven by consumer demand and regulatory incentives.
Biopesticide Market Recent Developments:
- Bayer’s Vynyty Citrus® (2022): Bayer launched Vynyty Citrus®, a bioinsecticide using pheromones to control citrus pests, reducing chemical use. It targets fruit flies with high efficacy.
- Corteva’s Reklemel™ Active (2023): Corteva introduced Reklemel™, a bioinsecticide for lepidopteran pests in row crops, offering sustainable pest control with minimal environmental impact.
List of Top Biopesticides Companies:
- FMC Corporation
- Isagro
- Koppert Biological Systems
- Marrone Bio Innovations
- Novozymes Biologicals
Biopesticides Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Biopesticides Market Size in 2025 | US$9.590 billion |
| Biopesticides Market Size in 2030 | US$14.752 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 9.00% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Biopesticides Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Different segments covered under the biopesticides market report are as below:
By Type
- Bio-Insecticides
- Bio-Nematicides
- Bio-Herbicides
- Bio-Fungicides
- Others
By Crop Type
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Oilseeds and Pulses
- Cereals and Grains
- Others
By Application:
- Foliar Spray
- Soil Treatment
- Seed Treatment
- Post-Harvest
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- India
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Others