The Development of 5G Ecosystem in Japan: A Road to Better Connectivity

The Japanese government in April 2022 set a goal for the 5G ecosystem, according to which 99% of the population is anticipated to be serviced by 5G networks by the end of the fiscal year 2030. The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC) is the leading organization for overseeing this objective getting fulfilled. The MIC had granted NTT Docomo, KDDI au, SoftBank, and a more recent newcomer, Rakuten Mobile, access to the country's 5G spectrum in 2019 for the construction of 5G networks. These four mobile network operators began offering 5G commercial service in all prefectures by the end of March 2021. By 2022, more than 20,000 mmWave gNodeBs have been installed among the nation's four main carriers, and more are obligated to the Japan Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications and will be installed by the beginning of 2024.
Get In-Depth Analysis of the 5G Revolution
This article covers the fundamentals of Japan's 5G rollout. Our full market reports provide the granular data and strategic insights you need to navigate the global 5G landscape.- ? Detailed Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- ? Competitive Landscape & Key Player Analysis
- ? Infrastructure Breakdowns & Regional Trends
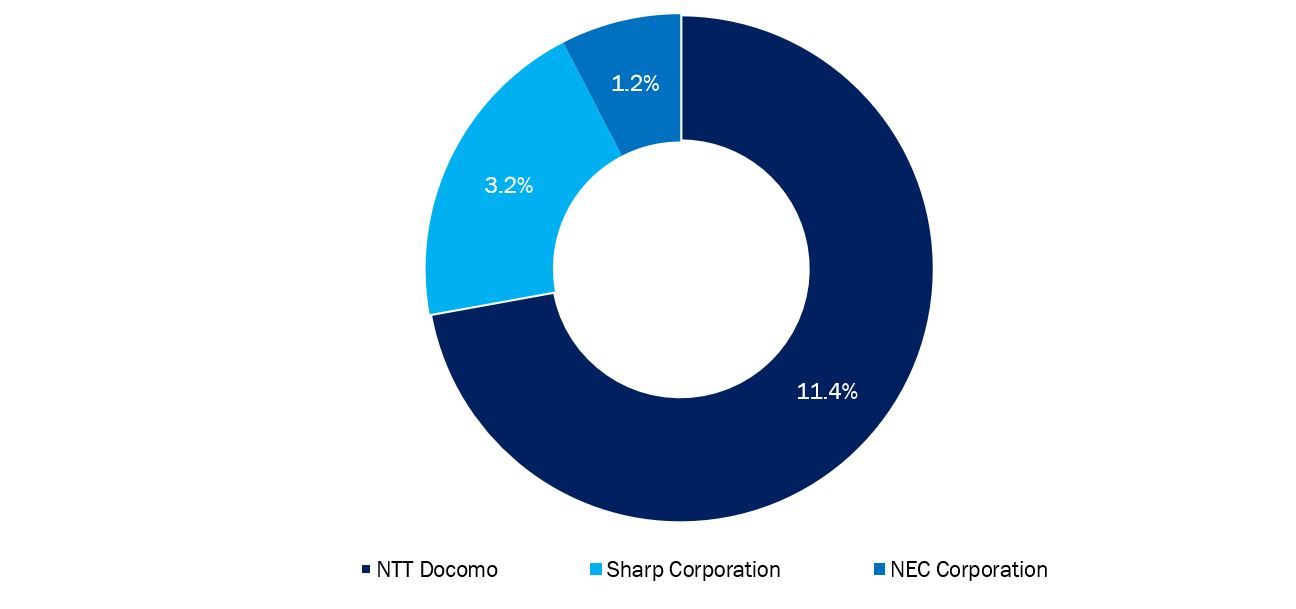
According to a survey conducted by Cyber Creative Institute in April 2021, NTT DOCOMO is ranked third globally in terms of the number of 5G essential patents, while Japan is ranked second by nationality among the top 10 nations. According to this analysis, NTT DOCOMO tops the list of international telecom carriers. About 15% of the standard necessary 5G patents are held by Japanese companies; however, an MNO, NTT DOCOMO, controls about 11.4% of the total, followed by Sharp Corporation with 3.2% and NEC Corporation with 1.2% share.
Japanese Companies' Share of Standard Essential Patents for 5G
The Global System for Mobile Communications Association reported that Japan permits operators to install 5G base stations on top of traffic lights, hastening the rollout of 5G across the country. When micro cells are put in place and network density is increased, 21 higher-capacity use cases can develop. According to the GSMA APAC 5G Forum, the penetration of 5G connections in Japan is anticipated to grow from 153% in 2021 to 154% in 2025. The percentage of 5G smartphone adoptions is anticipated to rise from 71% in 2021 to 81% in 2025, and the 5G subscriber penetration is predicted to increase from 87% in 2021 to 88% in 2025. The same source has also reported the technology mix share of 5G in the country to be 12% in 2021, which is anticipated to increase to 68% by 2024.
Japan Technology Mix, %, 2021 and 2025
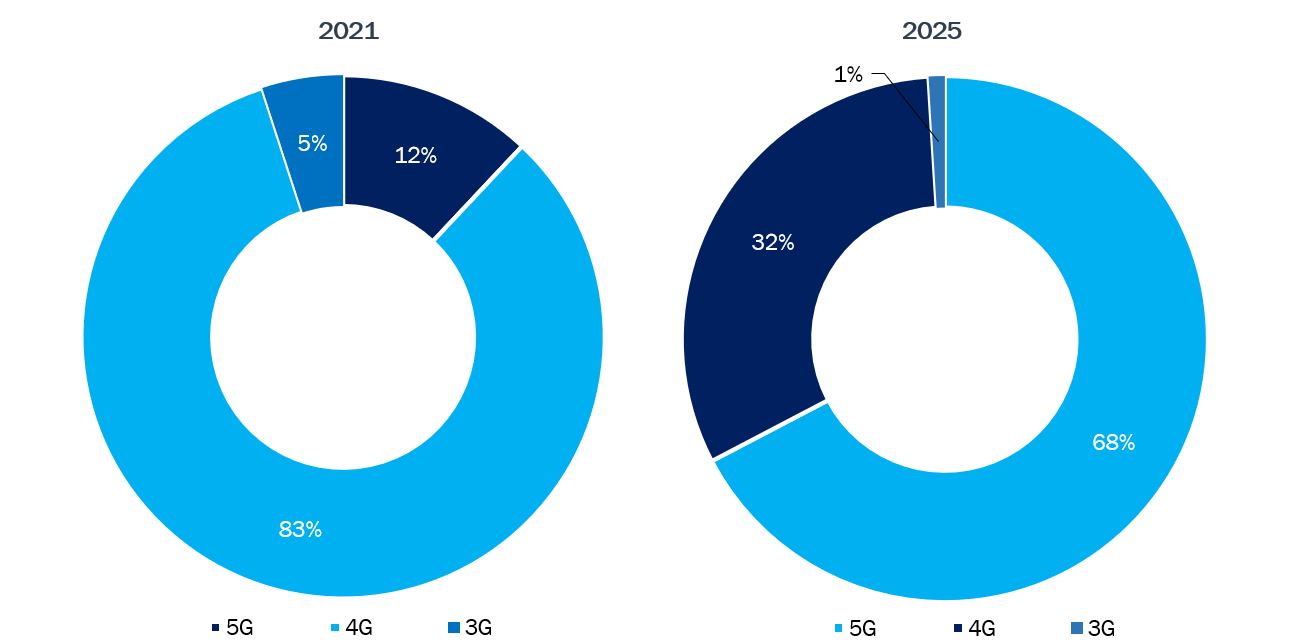
Source: GSMA APAC 5G Forum
The four major 5G network carriers in Japan are anticipated to invest a significant sum, to the tune of $14 billion, to expand the 5G network in the country. This covers base stations, servers, and fiber optic investments. By 2025, NTT Docomo plans to spend over $7 billion to extend its network to 97% of the country's populated areas, KDDI plans to spend over $4 billion to accomplish the same for about 93% of the population, Softbank plans to spend over $1.9 billion to reach nearly 64% of the population, and Rakuten Mobile plans to spend over $1.8 billion to do the same for roughly 56% of the population.
Number of 5G Base Stations in Japan, 2020 to 2023
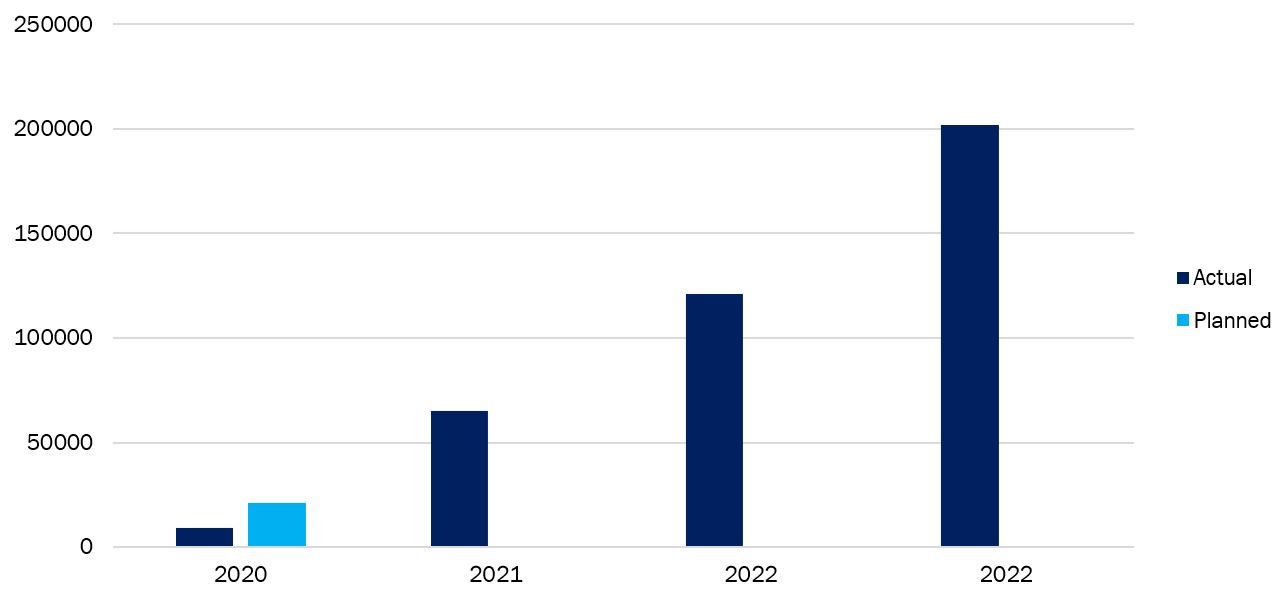 Source: MIC, Japan
Source: MIC, Japan
Analyze the 5G Infrastructure Market
The rollout of 5G base stations is a key driver of the entire ecosystem. Get our in-depth report on the 5G Base Station Equipment Market for detailed forecasts and competitive analysis.Planned 5G Base Stations in Japan by 2025
|
Company |
Planned 3.7/4.5 GHz spectrum base stations by 2025 |
Planned 28 GHz base stations by 2025 |
|
NTT Docomo |
8001 |
5001 |
|
KDDI au |
30107 |
12756 |
|
SoftBank |
7355 |
3855 |
|
Rakuten Mobile |
15787 |
7948 |
|
Total |
61250 |
29560 |
Source: MIC, Japan
For instance, according to the integrated report 2020, NTT Docomo sought to develop a fast, large-capacity 5G network across the country, fully utilizing new frequency bands, in order to create new value. In FY2020, 500 cities will be covered by the 5G network. With a target of installing 10,000 5G base stations by June 2021 and 20,000 5G base stations by March 2022, NTT Docomo invested a total of 1 trillion yen in the building of the 5G network between FY2019 and FY2023.
Although macrocells are used in 5G networks, the advent of higher spectrum bands would require denser network deployments to serve increased traffic volumes; hence, the deployment of small cells would be crucial. The deployment of 5G will be made much easier by streamlining the small cell deployment procedure. For the same reason, Japan has allowed operators to mount 5G base stations atop traffic signals since 2022, which has accelerated 5G deployments throughout the nation, as reported by GMSA. Higher-capacity use cases will be able to thrive as tiny cells are deployed and network density is enhanced.
Further, in order to meet the different needs of communication carriers and companies in the 5G era, DOCOMO collaborated with 12 global suppliers to advance open radio access networks (Open RAN), which enable flexible network development, and develop them abroad into the "5G Open RAN Ecosystem. In order to support NTT DOCOMO's Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) expansion plans, Samsung Electronics announced in November 2022 that provide a range of 5G radios, including 3.7 GHz, 4.5 GHz, and 28 GHz, to its existing 3.4 GHz radio. These radios will cover the entire Time Division Duplex (TDD) spectrum bands held by the operator. In order to advance 5G commercial services, NTT DOCOMO, INC. and Korean telecom operator SK Telecom (SKT) agreed to work together regarding the technology for telecommunications infrastructure. The use of millimeter-wave technology, energy-efficient networks, open RAN/vRAN, and 5G Stand Alone is some of the specific technical topics that will be taken into account.
Moreover, in August 2022, Nokia announced the launch of an Industrial 5G field router that supports the local band and is approved for the Japanese market, and is expanding its industrial portfolio of ruggedized devices. Japan's asset-intensive businesses will be able to use the field router to take advantage of dedicated coverage and capacity using the recently announced 5G n79 band or other 4.9G/LTE spectrum bands for local networks. Greater operational flexibility will help ports, manufacturers, energy, transportation, storage, and logistics businesses adapt to the needs of a market that is changing quickly.
The 5G operators in the country have launched standalone networks to enable design simplicity, boost security, and save costs. In addition to enabling customization, 5G standalone is anticipated to create new service and income options for users. For instance, in August 2022, NTT DOCOMO, Inc. unveiled the first commercial 5G Standalone network in the world, also known as 5G NR Dual Connectivity, letting smartphones simultaneously use mid-band (sub-6 GHz) and mmWave frequencies (NR-DC). The Qualcomm wireless technology business, which was eager to demonstrate that smartphones running on its Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 platform can utilize the full speed of the new network, collaborated on the announcement. Users of the Sharp AQUOS R7, Samsung Galaxy S22, Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra, or Sony's Xperia 1 IV, which are all equipped with the Snapdragon® 8 Gen 1 Mobile Platform and the Snapdragon X65 5G Modem-RF System, are already experiencing download speeds of up to 4.9 Gbps and upload speeds of up to 1.1 Gbps, even in congested areas.
Additionally, the introduction of a 5G MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) site in the Kanto region and the nationwide deployment of MEC servers in Japan were both announced by SoftBank Corporation in May 2022. SoftBank 5G MEC provides a low-latency, high-quality (low-jitter), and highly secure service experience using 5G SA (5G Stand Alone) commercial services. SoftBank is anticipated to address social issues and progress the industry as a digital platform provider in the Beyond 5G future by fostering the digital transformation (DX) of diverse industries and reaching Digital Twin*2.
Although 5GC software is essential for managing cell phone networks, domestic production and cost control are continuous issues that prevent associated technologies, including private 5G, from becoming a reality. To accomplish this, the University of Tokyo, Internet Initiative Japan, APRESIA, and Fujitsu Limited in November 2022, created open-source software for the Private 5G Mobile System, bringing the 5G core network (5GC), the essential component of the 5G mobile networks, to domestic production. The partners' initiative was carried out as a component of NEDO's Research and Development Project of the Feasibility Study of Enhanced Infrastructures for Post-5G Information and Communication Systems. As a result, 5G base stations and terminal equipment produced by each company will be integrated with the 5GC technology created through this project to provide solutions for private 5G networks that will be continually released by APRESIA and Fujitsu. Using the 5GC and the public 5G networks that IIJ offers as a mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) through roaming, IIJ will also encourage the creation of communication services that can utilize a variety of private 5G networks.
The 5G launch has provided a number of new options for smartphone makers due to rising consumer and app developer demand. With the help of the Internet of Things, 5G technology has enabled extremely fast speeds as well as a plethora of new applications. Customers of 5G devices in Japan have access to a variety of mmWave devices, including high-end smartphones from Apple, Samsung, Sony, Sharp Corporation, Fujitsu, and Google, as well as substantial carrier momentum for the technology. A number of new 5G devices launches have been announced by the major players. For instance, for the Japanese market, Samsung unveiled a new version of the Galaxy A23 5G in November 2022, which features a smaller screen, a MediaTek Dimensity 700 chipset, and an IP68 rating. It has a 5.8-inch TFT LCD with HD+ resolution and a waterdrop notch for its 5 MP selfie camera. In February 2022, Panasonic Corporation announced to introduction of new "TOUGHBOOK" rugged tablet "FZ-G2 series" and rugged PC "CF-33 series" models that are appropriate for outdoor and harsh situations for domestic enterprises.
Due to pressure from important stakeholders, including shareholders and customers, operators across the nation are moving more quickly toward more environmentally friendly operations. For instance, NTT Docomo and NTT Anode Energy Corp. inked a power purchase agreement (PPA) in March 2022 that was connected to a recently built solar power plant.
The cellular infrastructure in Japan is one of the most sophisticated in the world. The introduction of the 5G ecosystem in the nation has further improved communication thanks to a quicker network, improved signal strength, minimal latency, seamless connectivity, and quick data speeds. Massive machine-type communication (mMTC) is a feature of 5G that enables tens of billions of network-capable devices to connect wirelessly which benefits various end-user industries. The rising use of connectivity, internet applications, and new product launches have all contributed to the growth of companies in the 5G device market in Japan. Additionally, major 5G network carriers' investments to upgrade current infrastructure for 5G, including base stations, modems, towers, and other supporting infrastructure, have accelerated the development of the 5G ecosystem in the nation. Furthermore, as the deployment of 5G technology has received encouraging signals, the rise of the 5G ecosystem is anticipated to create substantial prospects for different stakeholders.
Go from Insight to Action with Our 5G Market Research
You've seen the overview. Now, get the detailed data and strategic analysis you need to stay ahead in the telecommunications market. Each report includes comprehensive data, forecasts, and competitive analysis to empower your business decisions.Get in Touch
Interested in this topic? Contact our analysts for more details.
Latest Thought Articles

Top OSAT Companies Driving Semiconductor Assembly and Test Services Worldwide
Recently
EV Charging Stations Market Outlook: Smart Charging, Fast Charging, and Regional Expansion
Recently
Future of Corporate Wellness: Global Trends and Regional Outlook
Recently
Regional Breakdown of the Mechanical Keyboard Market: Who Leads and Why?
Recently