From Algorithms to Empathy: The Promise of Emotional AI

In 2023, Kate Crawford estimated the value of the emotional AI sector to be approximately $22 billion, with projections indicating a doubling of this figure by the year 2024.
Emotional AI Market, in US$ Billion
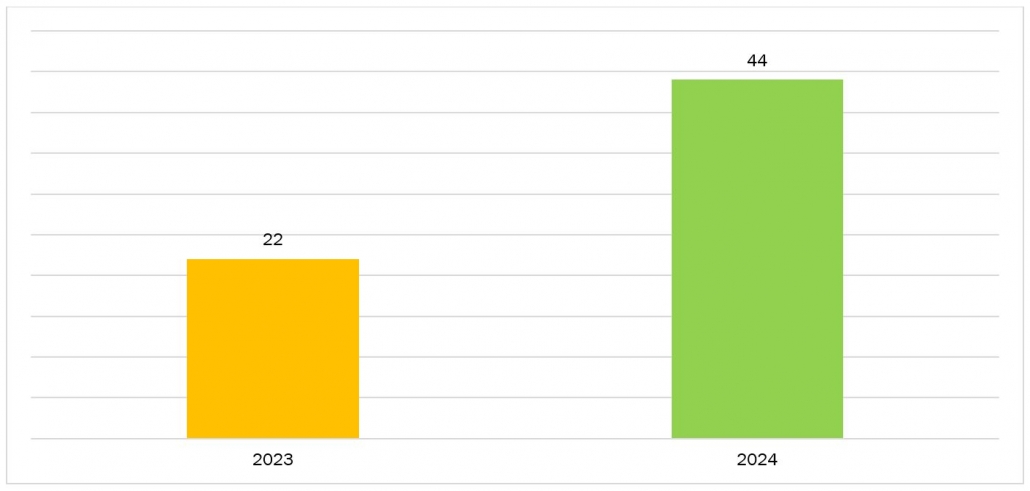 Source: PubMed Central
In today's digital age, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to reshape the way we interact with technology. From voice assistants to recommendation algorithms, AI permeates various aspects of our lives, offering convenience, efficiency, and personalized experiences. However, as technology evolves, so do our expectations. In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on imbuing AI systems with emotional intelligence, leading to the emergence of Emotional AI, also known as affective computing. This groundbreaking field seeks to bridge the gap between humans and machines by enabling computers to recognize, interpret, and respond to human emotions. In this article, we will delve into the transformative potential of Emotional AI, exploring its applications across industries, recent developments, and ethical considerations.
In February 2024, EIT Digital, along with 12 other prominent European institutions in education, research, and technology, introduced "EMAI4EU," a significant four-year endeavor aimed at educating professionals in the realm of artificial emotional intelligence. EIT Digital, renowned as a leading force in digital innovation across Europe, unveiled EMAI4EU, a fresh initiative spanning four years to enrich education in emotional artificial intelligence throughout Europe. This collaborative effort unites 13 esteemed European institutions to craft innovative degree programs and learning modules tailored to equip participants with advanced AI skills.
Understanding Emotional AI:
At its core, Emotional AI encompasses the integration of algorithms, machine learning techniques, and sensor technologies to enable machines to perceive and understand human emotions. This involves analyzing various cues, including facial expressions, vocal intonations, body language, and textual sentiment. By deciphering these emotional signals, Emotional AI systems can infer users' mental states and tailor responses accordingly.
One of the key challenges in developing Emotional AI lies in creating algorithms capable of accurately recognizing and interpreting complex human emotions. This requires a multidisciplinary approach, drawing insights from psychology, neuroscience, computer vision, natural language processing, and other fields. Researchers leverage datasets comprising labeled emotional expressions to train machine learning models, enabling them to recognize patterns and make predictions about users' emotional states.
Applications Across Industries:
The potential applications of Emotional AI span a wide range of industries, each with unique opportunities to leverage emotional intelligence in human-machine interactions:
1. Customer Service:
In the realm of customer service, Emotional AI holds the promise of revolutionizing the way businesses engage with their customers. Chatbots and virtual assistants equipped with Emotional AI capabilities can understand users' emotions, empathize with their concerns, and provide tailored assistance. For example, a chatbot integrated into a retail website can detect frustration in a customer's tone and offer personalized solutions to address their issue, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Healthcare:
Emotional AI has significant implications for the healthcare sector, particularly in the realm of mental health. By analyzing patients' emotional cues during therapy sessions, AI-driven systems can provide valuable insights into their psychological well-being and facilitate personalized interventions. For instance, a virtual therapist equipped with Emotional AI can detect signs of anxiety or depression in a patient's speech patterns and offer coping strategies or recommend further treatment.
3. Education:
In the field of education, Emotional AI has the potential to revolutionize personalized learning experiences. Adaptive learning platforms powered by Emotional AI algorithms can gauge students' emotional responses to educational content and adjust the curriculum accordingly. For example, if a student exhibits signs of frustration or confusion while solving a math problem, the system can offer additional explanations or alternative learning resources tailored to their needs, thereby optimizing learning outcomes.
4. Automotive:
In the automotive industry, Emotional AI is poised to transform the driving experience by enhancing safety and comfort. In-car systems equipped with emotion recognition capabilities can monitor drivers' emotional states and intervene when necessary to prevent accidents or mitigate risks. For instance, if a driver displays signs of drowsiness or distraction, the system can issue alerts, adjust the vehicle's settings, or even initiate autonomous driving mode to ensure safe navigation.
Recent Developments and Examples:
In recent years, there have been notable advancements in Emotional AI research and development, leading to innovative applications and technologies:
1. Amazon's Alexa Emotions:
Amazon, a leading player in the voice assistant market, is exploring Emotional AI capabilities for its popular Alexa virtual assistant. By integrating emotion recognition algorithms into Alexa-enabled devices, Amazon aims to make interactions with the assistant more empathetic and human-like. For example, Alexa may adjust its tone of voice or response based on the user's emotional state, providing a more personalized and engaging experience.
2. IBM Watson's Tone Analyzer:
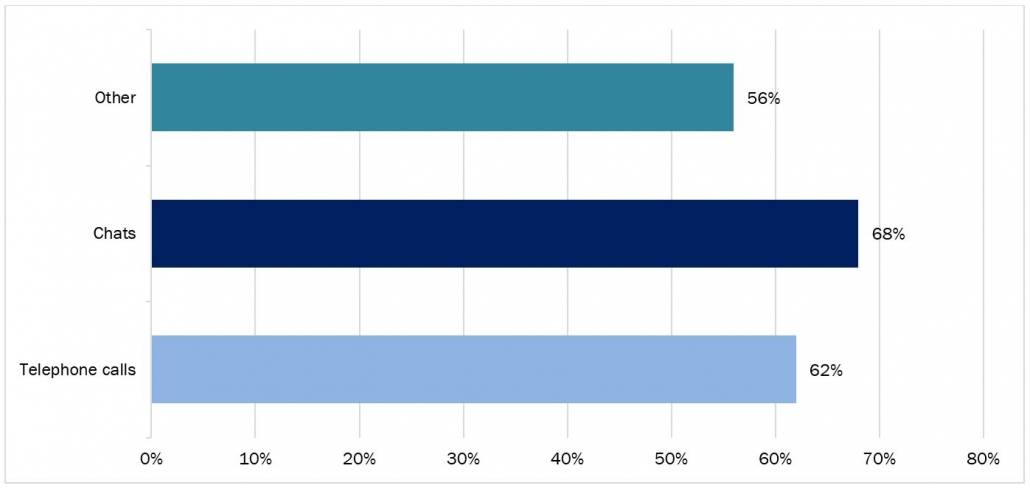
IBM Watson offers a Tone Analyzer tool that leverages Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to evaluate textual content and discern emotional tones. Businesses can use this tool to analyze customer feedback, social media posts, and other text-based data to gauge sentiment and tailor their communication strategies accordingly. For instance, a company may use the Tone Analyzer to identify areas of customer dissatisfaction and address them proactively, thereby improving brand perception and customer satisfaction. IBM Watson Assistant handles 62% of telephone calls, 68% of chats, and 56% of other queries received by IBM, in each month.
Percentage of Queries Handled by IBM Watson Assistant Monthly
Source: PubMed Central
In today's digital age, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to reshape the way we interact with technology. From voice assistants to recommendation algorithms, AI permeates various aspects of our lives, offering convenience, efficiency, and personalized experiences. However, as technology evolves, so do our expectations. In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on imbuing AI systems with emotional intelligence, leading to the emergence of Emotional AI, also known as affective computing. This groundbreaking field seeks to bridge the gap between humans and machines by enabling computers to recognize, interpret, and respond to human emotions. In this article, we will delve into the transformative potential of Emotional AI, exploring its applications across industries, recent developments, and ethical considerations.
In February 2024, EIT Digital, along with 12 other prominent European institutions in education, research, and technology, introduced "EMAI4EU," a significant four-year endeavor aimed at educating professionals in the realm of artificial emotional intelligence. EIT Digital, renowned as a leading force in digital innovation across Europe, unveiled EMAI4EU, a fresh initiative spanning four years to enrich education in emotional artificial intelligence throughout Europe. This collaborative effort unites 13 esteemed European institutions to craft innovative degree programs and learning modules tailored to equip participants with advanced AI skills.
Understanding Emotional AI:
At its core, Emotional AI encompasses the integration of algorithms, machine learning techniques, and sensor technologies to enable machines to perceive and understand human emotions. This involves analyzing various cues, including facial expressions, vocal intonations, body language, and textual sentiment. By deciphering these emotional signals, Emotional AI systems can infer users' mental states and tailor responses accordingly.
One of the key challenges in developing Emotional AI lies in creating algorithms capable of accurately recognizing and interpreting complex human emotions. This requires a multidisciplinary approach, drawing insights from psychology, neuroscience, computer vision, natural language processing, and other fields. Researchers leverage datasets comprising labeled emotional expressions to train machine learning models, enabling them to recognize patterns and make predictions about users' emotional states.
Applications Across Industries:
The potential applications of Emotional AI span a wide range of industries, each with unique opportunities to leverage emotional intelligence in human-machine interactions:
1. Customer Service:
In the realm of customer service, Emotional AI holds the promise of revolutionizing the way businesses engage with their customers. Chatbots and virtual assistants equipped with Emotional AI capabilities can understand users' emotions, empathize with their concerns, and provide tailored assistance. For example, a chatbot integrated into a retail website can detect frustration in a customer's tone and offer personalized solutions to address their issue, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Healthcare:
Emotional AI has significant implications for the healthcare sector, particularly in the realm of mental health. By analyzing patients' emotional cues during therapy sessions, AI-driven systems can provide valuable insights into their psychological well-being and facilitate personalized interventions. For instance, a virtual therapist equipped with Emotional AI can detect signs of anxiety or depression in a patient's speech patterns and offer coping strategies or recommend further treatment.
3. Education:
In the field of education, Emotional AI has the potential to revolutionize personalized learning experiences. Adaptive learning platforms powered by Emotional AI algorithms can gauge students' emotional responses to educational content and adjust the curriculum accordingly. For example, if a student exhibits signs of frustration or confusion while solving a math problem, the system can offer additional explanations or alternative learning resources tailored to their needs, thereby optimizing learning outcomes.
4. Automotive:
In the automotive industry, Emotional AI is poised to transform the driving experience by enhancing safety and comfort. In-car systems equipped with emotion recognition capabilities can monitor drivers' emotional states and intervene when necessary to prevent accidents or mitigate risks. For instance, if a driver displays signs of drowsiness or distraction, the system can issue alerts, adjust the vehicle's settings, or even initiate autonomous driving mode to ensure safe navigation.
Recent Developments and Examples:
In recent years, there have been notable advancements in Emotional AI research and development, leading to innovative applications and technologies:
1. Amazon's Alexa Emotions:
Amazon, a leading player in the voice assistant market, is exploring Emotional AI capabilities for its popular Alexa virtual assistant. By integrating emotion recognition algorithms into Alexa-enabled devices, Amazon aims to make interactions with the assistant more empathetic and human-like. For example, Alexa may adjust its tone of voice or response based on the user's emotional state, providing a more personalized and engaging experience.
2. IBM Watson's Tone Analyzer:
IBM Watson offers a Tone Analyzer tool that leverages Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to evaluate textual content and discern emotional tones. Businesses can use this tool to analyze customer feedback, social media posts, and other text-based data to gauge sentiment and tailor their communication strategies accordingly. For instance, a company may use the Tone Analyzer to identify areas of customer dissatisfaction and address them proactively, thereby improving brand perception and customer satisfaction. IBM Watson Assistant handles 62% of telephone calls, 68% of chats, and 56% of other queries received by IBM, in each month.
Percentage of Queries Handled by IBM Watson Assistant Monthly
 Source: IBM Report
3. Affectiva's Automotive AI:
Affectiva, a pioneer in Emotional AI, collaborates with automotive manufacturers to develop in-car systems that recognize and respond to drivers' emotions. By integrating emotion recognition sensors into vehicles, Affectiva's Automotive AI technology can detect a range of emotional states, including stress, fatigue, and distraction. For example, if a driver displays signs of road rage or frustration, the system may activate calming music, adjust the ambient lighting, or provide soothing voice prompts to help alleviate tension and promote safe driving.
On May 25, 2021, Smart Eye revealed its acquisition of Affectiva, merging the two entities to spearhead advancements in the automotive sector. Through the integration of their respective technologies, these two trailblazers aim to accelerate the delivery of automotive-grade AI solutions to meet the demands of the evolving interior sensing market.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations:
While Emotional AI holds immense promise to humanize technology and improve human-machine interactions, it also raises important ethical and privacy considerations:
1. Data Privacy:
Emotional AI systems rely on vast amounts of personal data, including facial images, voice recordings, and textual content, to analyze and interpret users' emotions. Safeguarding this data and ensuring user privacy are paramount to building trust and fostering widespread adoption of Emotional AI technologies. Companies must adhere to strict data protection regulations and implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive information.
2. Algorithmic Bias:
Like all AI systems, Emotional AI algorithms are susceptible to bias, which can manifest in various forms, including gender, racial, and cultural biases. Biased algorithms may lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, exacerbating existing societal inequalities. To mitigate bias in Emotional AI systems, researchers and developers must carefully design and evaluate algorithms, prioritize diversity and inclusivity in training datasets, and implement transparency and accountability measures to address bias-related issues.
The burgeoning market for emotion recognition is projected to reach $3.8 billion by the year 2025. Emotional AI represents a paradigm shift in the field of artificial intelligence, enabling machines to understand and respond to human emotions in increasingly sophisticated ways. As advancements continue and ethical frameworks evolve, Emotional AI has the potential to enrich human-machine interactions across various domains, from customer service to healthcare and beyond. By harnessing the power of Emotional AI, we can create more empathetic, personalized, and inclusive technologies that enhance our lives and improve our well-being. As we embark on this transformative journey, it is essential to prioritize ethical considerations, uphold privacy rights, and ensure that Emotional AI serves the best interests of humanity.
Source: IBM Report
3. Affectiva's Automotive AI:
Affectiva, a pioneer in Emotional AI, collaborates with automotive manufacturers to develop in-car systems that recognize and respond to drivers' emotions. By integrating emotion recognition sensors into vehicles, Affectiva's Automotive AI technology can detect a range of emotional states, including stress, fatigue, and distraction. For example, if a driver displays signs of road rage or frustration, the system may activate calming music, adjust the ambient lighting, or provide soothing voice prompts to help alleviate tension and promote safe driving.
On May 25, 2021, Smart Eye revealed its acquisition of Affectiva, merging the two entities to spearhead advancements in the automotive sector. Through the integration of their respective technologies, these two trailblazers aim to accelerate the delivery of automotive-grade AI solutions to meet the demands of the evolving interior sensing market.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations:
While Emotional AI holds immense promise to humanize technology and improve human-machine interactions, it also raises important ethical and privacy considerations:
1. Data Privacy:
Emotional AI systems rely on vast amounts of personal data, including facial images, voice recordings, and textual content, to analyze and interpret users' emotions. Safeguarding this data and ensuring user privacy are paramount to building trust and fostering widespread adoption of Emotional AI technologies. Companies must adhere to strict data protection regulations and implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive information.
2. Algorithmic Bias:
Like all AI systems, Emotional AI algorithms are susceptible to bias, which can manifest in various forms, including gender, racial, and cultural biases. Biased algorithms may lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, exacerbating existing societal inequalities. To mitigate bias in Emotional AI systems, researchers and developers must carefully design and evaluate algorithms, prioritize diversity and inclusivity in training datasets, and implement transparency and accountability measures to address bias-related issues.
The burgeoning market for emotion recognition is projected to reach $3.8 billion by the year 2025. Emotional AI represents a paradigm shift in the field of artificial intelligence, enabling machines to understand and respond to human emotions in increasingly sophisticated ways. As advancements continue and ethical frameworks evolve, Emotional AI has the potential to enrich human-machine interactions across various domains, from customer service to healthcare and beyond. By harnessing the power of Emotional AI, we can create more empathetic, personalized, and inclusive technologies that enhance our lives and improve our well-being. As we embark on this transformative journey, it is essential to prioritize ethical considerations, uphold privacy rights, and ensure that Emotional AI serves the best interests of humanity.
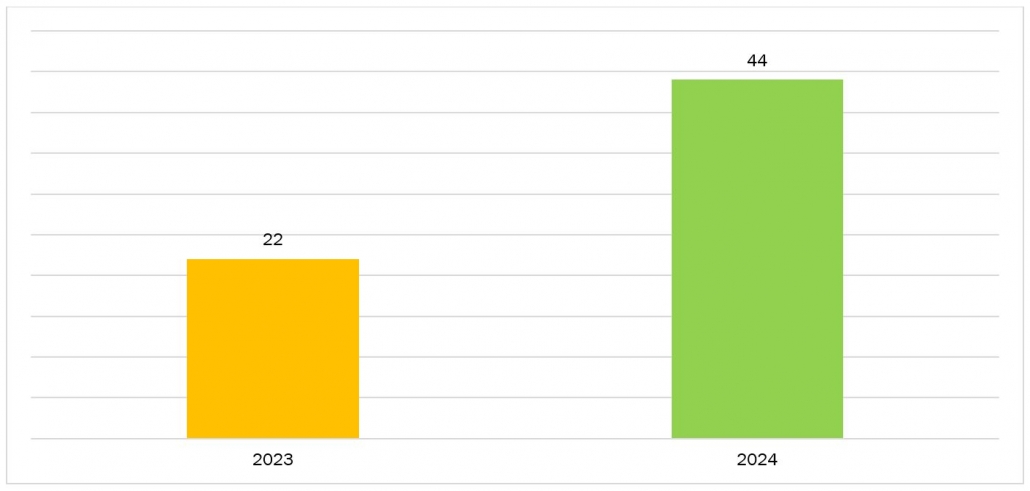 Source: PubMed Central
In today's digital age, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to reshape the way we interact with technology. From voice assistants to recommendation algorithms, AI permeates various aspects of our lives, offering convenience, efficiency, and personalized experiences. However, as technology evolves, so do our expectations. In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on imbuing AI systems with emotional intelligence, leading to the emergence of Emotional AI, also known as affective computing. This groundbreaking field seeks to bridge the gap between humans and machines by enabling computers to recognize, interpret, and respond to human emotions. In this article, we will delve into the transformative potential of Emotional AI, exploring its applications across industries, recent developments, and ethical considerations.
Source: PubMed Central
In today's digital age, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to reshape the way we interact with technology. From voice assistants to recommendation algorithms, AI permeates various aspects of our lives, offering convenience, efficiency, and personalized experiences. However, as technology evolves, so do our expectations. In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on imbuing AI systems with emotional intelligence, leading to the emergence of Emotional AI, also known as affective computing. This groundbreaking field seeks to bridge the gap between humans and machines by enabling computers to recognize, interpret, and respond to human emotions. In this article, we will delve into the transformative potential of Emotional AI, exploring its applications across industries, recent developments, and ethical considerations.
Explore the Emotional AI Market
Discover the full potential of Emotional AI with our comprehensive market report, offering detailed insights into market size, growth forecasts, and key industry trends.- ? Market Size & Growth Projections
- ? Competitive Landscape Analysis
- ? Emerging Applications & Opportunities
Dive into the AI Chatbot Market
Learn how Emotional AI is transforming customer service with our in-depth AI Chatbot Market report, covering trends, technologies, and growth opportunities.Discover AI in Automotive
Learn how Emotional AI is shaping the future of driving with our detailed report on AI in the Automotive Market, covering innovations and market trends. Source: IBM Report
3. Affectiva's Automotive AI:
Affectiva, a pioneer in Emotional AI, collaborates with automotive manufacturers to develop in-car systems that recognize and respond to drivers' emotions. By integrating emotion recognition sensors into vehicles, Affectiva's Automotive AI technology can detect a range of emotional states, including stress, fatigue, and distraction. For example, if a driver displays signs of road rage or frustration, the system may activate calming music, adjust the ambient lighting, or provide soothing voice prompts to help alleviate tension and promote safe driving.
On May 25, 2021, Smart Eye revealed its acquisition of Affectiva, merging the two entities to spearhead advancements in the automotive sector. Through the integration of their respective technologies, these two trailblazers aim to accelerate the delivery of automotive-grade AI solutions to meet the demands of the evolving interior sensing market.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations:
While Emotional AI holds immense promise to humanize technology and improve human-machine interactions, it also raises important ethical and privacy considerations:
1. Data Privacy:
Emotional AI systems rely on vast amounts of personal data, including facial images, voice recordings, and textual content, to analyze and interpret users' emotions. Safeguarding this data and ensuring user privacy are paramount to building trust and fostering widespread adoption of Emotional AI technologies. Companies must adhere to strict data protection regulations and implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive information.
2. Algorithmic Bias:
Like all AI systems, Emotional AI algorithms are susceptible to bias, which can manifest in various forms, including gender, racial, and cultural biases. Biased algorithms may lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, exacerbating existing societal inequalities. To mitigate bias in Emotional AI systems, researchers and developers must carefully design and evaluate algorithms, prioritize diversity and inclusivity in training datasets, and implement transparency and accountability measures to address bias-related issues.
The burgeoning market for emotion recognition is projected to reach $3.8 billion by the year 2025. Emotional AI represents a paradigm shift in the field of artificial intelligence, enabling machines to understand and respond to human emotions in increasingly sophisticated ways. As advancements continue and ethical frameworks evolve, Emotional AI has the potential to enrich human-machine interactions across various domains, from customer service to healthcare and beyond. By harnessing the power of Emotional AI, we can create more empathetic, personalized, and inclusive technologies that enhance our lives and improve our well-being. As we embark on this transformative journey, it is essential to prioritize ethical considerations, uphold privacy rights, and ensure that Emotional AI serves the best interests of humanity.
Source: IBM Report
3. Affectiva's Automotive AI:
Affectiva, a pioneer in Emotional AI, collaborates with automotive manufacturers to develop in-car systems that recognize and respond to drivers' emotions. By integrating emotion recognition sensors into vehicles, Affectiva's Automotive AI technology can detect a range of emotional states, including stress, fatigue, and distraction. For example, if a driver displays signs of road rage or frustration, the system may activate calming music, adjust the ambient lighting, or provide soothing voice prompts to help alleviate tension and promote safe driving.
On May 25, 2021, Smart Eye revealed its acquisition of Affectiva, merging the two entities to spearhead advancements in the automotive sector. Through the integration of their respective technologies, these two trailblazers aim to accelerate the delivery of automotive-grade AI solutions to meet the demands of the evolving interior sensing market.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations:
While Emotional AI holds immense promise to humanize technology and improve human-machine interactions, it also raises important ethical and privacy considerations:
1. Data Privacy:
Emotional AI systems rely on vast amounts of personal data, including facial images, voice recordings, and textual content, to analyze and interpret users' emotions. Safeguarding this data and ensuring user privacy are paramount to building trust and fostering widespread adoption of Emotional AI technologies. Companies must adhere to strict data protection regulations and implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive information.
2. Algorithmic Bias:
Like all AI systems, Emotional AI algorithms are susceptible to bias, which can manifest in various forms, including gender, racial, and cultural biases. Biased algorithms may lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, exacerbating existing societal inequalities. To mitigate bias in Emotional AI systems, researchers and developers must carefully design and evaluate algorithms, prioritize diversity and inclusivity in training datasets, and implement transparency and accountability measures to address bias-related issues.
The burgeoning market for emotion recognition is projected to reach $3.8 billion by the year 2025. Emotional AI represents a paradigm shift in the field of artificial intelligence, enabling machines to understand and respond to human emotions in increasingly sophisticated ways. As advancements continue and ethical frameworks evolve, Emotional AI has the potential to enrich human-machine interactions across various domains, from customer service to healthcare and beyond. By harnessing the power of Emotional AI, we can create more empathetic, personalized, and inclusive technologies that enhance our lives and improve our well-being. As we embark on this transformative journey, it is essential to prioritize ethical considerations, uphold privacy rights, and ensure that Emotional AI serves the best interests of humanity.
Stay Ahead with Our AI Market Research
You've explored the potential of Emotional AI. Now, dive deeper with our comprehensive reports on related AI markets to stay ahead of industry trends. Each report provides in-depth data, forecasts, and competitive analysis to empower your business decisions.Get in Touch
Interested in this topic? Contact our analysts for more details.
Latest Thought Articles

Top OSAT Companies Driving Semiconductor Assembly and Test Services Worldwide
Recently
EV Charging Stations Market Outlook: Smart Charging, Fast Charging, and Regional Expansion
Recently
Future of Corporate Wellness: Global Trends and Regional Outlook
Recently
Regional Breakdown of the Mechanical Keyboard Market: Who Leads and Why?
Recently