Top 10 Emerging Food Technologies in The World

Top 10 Emerging Food Technologies
Technology is causing a transformative shift in the food sector, influencing its growth, production, global distribution, and supply chain. Recent advancements in food tech trends are reshaping how the industry manages production, distribution, and consumption, showcasing the impact of technologies like AI and automation. A prominent trend in the food industry is the shift among consumers towards alternative protein sources, including lab-grown food. The pandemic has heightened awareness about nutrition and health, driving an increased demand for nutraceuticals and personalized nutrition. The rise of food e-commerce, spurred by the COVID-19 situation, is another significant trend. Additionally, growing concerns about food safety are influencing food transparency throughout the value chain. As digitization becomes integral to the food and beverage industry, companies are embracing restaurant digitization, digital food management, and food robotics to enhance operational efficiency. Food brands are actively addressing food waste reduction and adopting zero-waste practices. Notably, 3D food printers are emerging as a key component in the realm of food science and technology, facilitating major trends such as meat alternatives and personalized nutrition.Explore the Personalized Nutrition Market
Discover how consumer demand for health-focused diets is driving innovation. Our in-depth report on the Personalized Nutrition Market provides insights into trends, forecasts, and key players.The Top 10 Emerging Food Technologies Are:
- Ghost Kitchens
- Robotics in Food
- Smart and Sustainable Packaging
- Plant Meat
- Smart Sensors
- Probiotic Drinks
- Forward Osmosis
- Nutraceuticals
- 3D Food Printers
- Restaurant Digitization
1. Ghost Kitchens
Ghost kitchens, also known as virtual kitchens or cloud kitchens, represent a modern and innovative concept in the food service industry. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar restaurants, ghost kitchens operate solely for online food delivery and takeaway services, eliminating the need for a physical dine-in space. These kitchens focus on efficiently preparing and fulfilling orders placed through various online platforms. The key characteristic of ghost kitchens is their absence of a traditional storefront or customer-facing space. Instead, they leverage technology and digital platforms to reach customers directly. This model enables greater flexibility for chefs and restaurant owners, as they can experiment with diverse menus and culinary concepts without the constraints of a physical location. Ghost kitchens capitalize on the growing trend of food delivery and the convenience sought by modern consumers. By streamlining operations and reducing overhead costs associated with maintaining a traditional restaurant space, ghost kitchens can offer a wide range of cuisines and dishes at competitive prices. Overall, the ghost kitchen concept embodies the intersection of technology, culinary innovation, and evolving consumer preferences, shaping the future landscape of the food service industry. The Government of Delhi, in its Cloud Kitchen Policy, released in April 2022, stated that at that time, 20,000 cloud kitchens operated in Delhi, and are growing at a 20% growth rate every year.2. Robotics in Food
The food industry, a significant sector with high employment rates, faces challenges in maintaining a seamless supply chain and ensuring food safety due to human intervention. To address these issues, industrial automation emerges as a crucial solution. In the present context, automation is indispensable for both food production and distribution. Manufacturers utilize automation and robotics in food production and packaging, leading to extended shelf life, enhanced food safety, and improved production cost efficiency. Automation incorporates technologies like AI, robotics, and drones. AI-based systems enable manufacturers to efficiently manage food production and delivery processes, enhancing operational efficiency. Through data analysis, food manufacturers can identify items and consumer demands, aligning production with these needs. The integration of robotics and AI software development enables companies to monitor critical operations such as processing, shipping, and storage, resulting in better oversight of food quality and safety. Many food service companies today are making significant investments in robotics and AI to streamline their operations. In a report by the government of the USA in 2020, industrial robot density in the food and beverage industry increased from 0.9 to 3.1 per 1 million hours, from 2003 to 2017.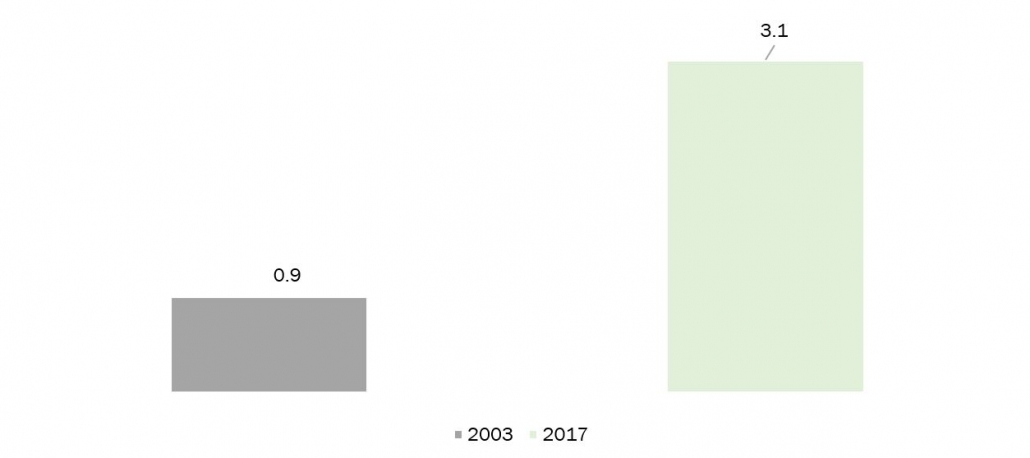 Source: USA Automation Report 2020
In September 2020, Bear Robotics, a U.S.-based startup, developed Servi, an autonomous robot tailored for food service. This robot collaborated with waitstaff to efficiently deliver dishes and beverages in tight spaces. By employing advanced camera and laser sensor navigation, Servi could navigate seamlessly without encountering blind spots.
Source: USA Automation Report 2020
In September 2020, Bear Robotics, a U.S.-based startup, developed Servi, an autonomous robot tailored for food service. This robot collaborated with waitstaff to efficiently deliver dishes and beverages in tight spaces. By employing advanced camera and laser sensor navigation, Servi could navigate seamlessly without encountering blind spots.
3. Smart and Sustainable Packaging
Smart and sustainable food packaging integrates innovative technologies and eco-friendly materials to revolutionize the way we package and consume food. These solutions aim to reduce environmental impact by utilizing recyclable or biodegradable materials, minimizing waste. Additionally, smart packaging incorporates technology like sensors to monitor freshness, temperature, and shelf life, ensuring food safety. By combining intelligence with sustainability, these packaging solutions contribute to a more efficient and environmentally conscious food industry. Biopolymers are gaining attention due to their environmentally friendly characteristics such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, and bio-based origins. These polymers can be obtained from food waste through extraction or fermentation processes. Polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) are two prominent biopolymers widely used in the production of biodegradable plastics. In a report on sustainable packaging by World Food India 2023, the demand for PLA is anticipated to double by 2023, while commercial PHA production reached 2.05 million tons in 2017. The global PHA market is forecasted to increase from USD 57 million in 2019 to USD 98 million by 2024.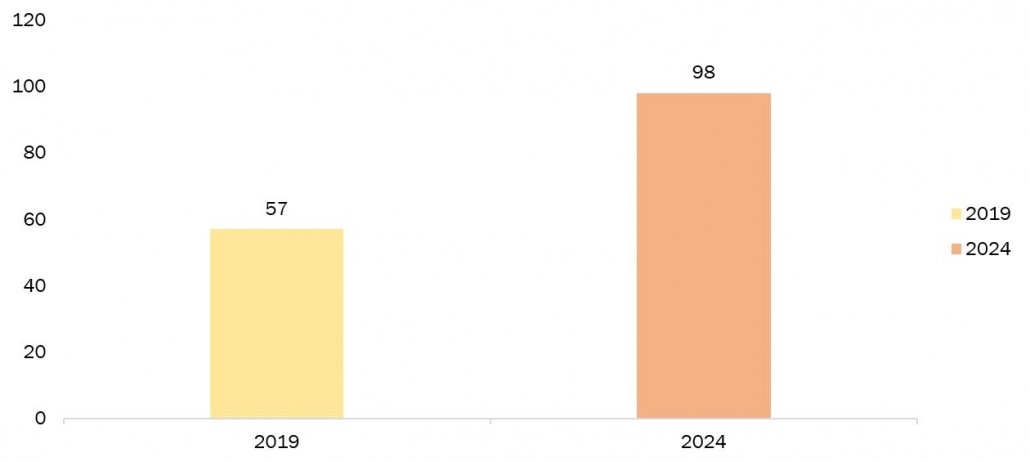 Source: World Food India Report
Source: World Food India Report
4. Plant Meat
Consumers are progressively embracing alternative protein sources, motivated by health and environmental concerns. This emerging trend in food technology encompasses options like cultured meat, lab-grown food, plant-based nutrition, edible insects, and mycoprotein. These alternatives offer significant nutritional value and resource efficiency throughout the production-to-consumption process, presenting a notable departure from conventional livestock-based protein sources. The Protein Brewery, a startup based in the Netherlands, creates FERMOTEIN, a unique lab-grown food without animal components. FERMOTEIN is produced by fermenting non-allergenic crops and fungi, enriching them with essential amino acids and fibre. With a 10% fat content and strong water-binding properties, this protein alternative delivers a taste resembling meat.Analyze the Plant-Based Meat Market
Understand the rise of alternative proteins. Our Plant-Based Meat Market report explores consumer trends, innovations, and growth opportunities.5. Smart Sensors
Smart sensors have simplified food production processes by providing essential insights to production managers. These sensors play a crucial role in tasks such as inventory counting, ingredient examination, temperature maintenance, and overall operational efficiency. In addition, businesses can extend the use of sensors to delivery vehicles, ensuring smooth distribution processes. The agri-food industry is gradually embracing Industry 4.0, with larger enterprises leading the way in adopting the latest technological advancements. However, the majority of agri-food companies in Europe, often SMEs, still lack smart sensor integration in their production setups.6. Probiotic Drinks
Fruits and vegetables are renowned for their abundance in nutrients, antioxidants, vitamins, dietary fiber, minerals, and bioactive molecules, constituting a vital element in a well-rounded diet with proven health benefits. The incorporation of probiotics into plant-based juices for the production of functional and nutraceutical food provides a cholesterol-free and allergen-free alternative to dairy probiotics, catering to individuals with lactose intolerance. Market trends in probiotic drinks are discussed, with a comprehensive list of current plant-based probiotic drinks available globally.7. Forward Osmosis
In the realm of food processing plants, the concentration process plays a crucial role in preserving food products until they reach consumers. Australia's CSIRO organization, in collaboration with a U.S. membrane technology company, has developed an innovative preservation processing technique utilizing membrane technology for liquid concentration, known as "forward osmosis." Forward osmosis represents a milder approach to concentrating food, requiring less energy and avoiding the use of heat. This method contributes to the natural retention of more nutrients, such as proteins and vitamins, during processing.8. Nutraceuticals
Growing concerns about the impact of dietary habits on health and increasing demand for essential nutrients to support a healthy lifestyle have become more pronounced, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. This heightened awareness among consumers is driving a significant trend in the food industry, placing nutraceuticals at the forefront. Nutraceuticals encompass a range of products, including nutritional supplements, functional foods, medicinal foods, and gut microbiome-enhancing foods like prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics. An example of innovation in this space is the US-based FoodTech startup Farmhand Organics, which specializes in crafting hand-made, naturally probiotic, plant-based fermented foods using organic ingredients. The startup's organic krauts and kimchi are designed to promote healthy digestion, contribute to maintaining balance in sleep and immunity, and offer nutrient-rich and flavourful options.Discover the Nutraceuticals Market
Explore the rise of health-focused foods. Our Nutraceuticals Market report provides insights into consumer trends and market growth.9. 3D Food Printers
3D food printers offer opportunities for customized diets and the development of protein-based meals, providing precision and reliability in nutritional content. While material extrusion remains the predominant method in food printing, startups are exploring innovative techniques such as laser and inkjet food printing, along with bioprinting. These inventive approaches enhance the quality and accuracy of 3D-printed food items. SavorEat, an Israeli startup, specializes in creating plant-based meat using a combination of chef robots, proprietary 3D printing technology, and non-GMO ingredients.10. Restaurant Digitization
Based on research conducted by the National Restaurant Association in 2020, the restaurant sector experienced a sales decline exceeding $120 billion, leading to the layoffs or furloughs of 8 million employees by May 2020. The incorporation of digital technology in restaurants not only enhances customer satisfaction but also optimizes operational processes, resulting in increased efficiency. To reduce direct person-to-person contact, restaurants are incorporating digital menus, self-service kiosks, and cashless payment options.Go from Insight to Action with Our Market Research
You've seen the overview. Now, get the detailed data and strategic analysis you need to stay ahead in the food and beverage market. Explore our related, in-depth reports. Each report includes comprehensive data, forecasts, and competitive analysis to empower your business decisions.Get in Touch
Interested in this topic? Contact our analysts for more details.
Latest Thought Articles

Top OSAT Companies Driving Semiconductor Assembly and Test Services Worldwide
Recently
EV Charging Stations Market Outlook: Smart Charging, Fast Charging, and Regional Expansion
Recently
Future of Corporate Wellness: Global Trends and Regional Outlook
Recently
Regional Breakdown of the Mechanical Keyboard Market: Who Leads and Why?
Recently