Report Overview
Frozen Vegetables Market Size, Highlights
Frozen Vegetables Market Size:
The frozen vegetables market will grow at a CAGR of 4.01% to reach US$23.41 billion in 2030 from US$19.23 billion in 2025.
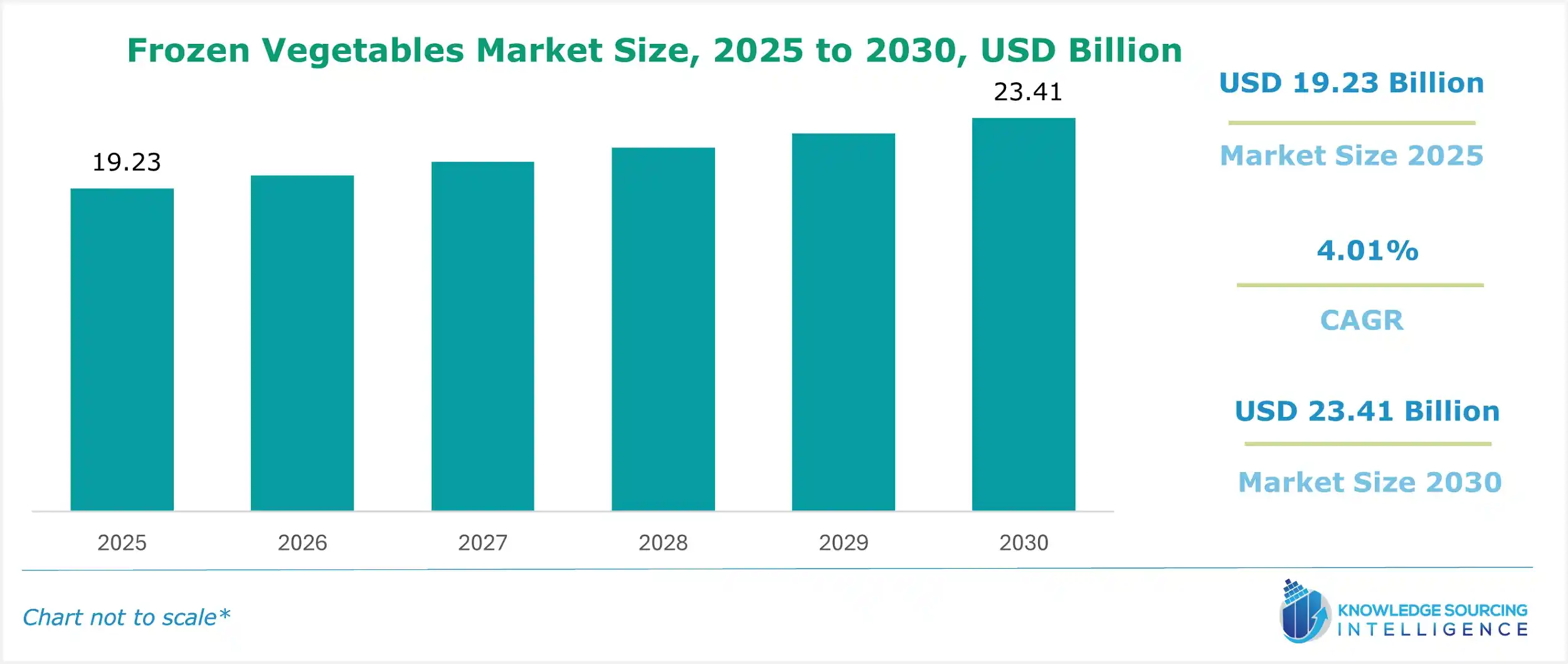
The global frozen vegetables market has evolved from a simple commodity sector to a sophisticated segment within the packaged food industry, characterized by continuous innovation and a strong orientation toward consumer convenience and health. This maturation is underscored by a critical divergence: a growing segment of consumers now views frozen produce not merely as a cost-effective substitute for fresh but as a premium, nutritionally reliable, and waste-reducing alternative. Industry players, particularly in established Western markets, are strategically recalibrating their product portfolios and supply chains to capitalize on the secular shift towards plant-based and ready-to-use meal components. The analytical imperative for industry experts lies in discerning how macro-economic pressures, supply chain logistics, and granular shifts in regulatory compliance collectively exert pressure and create opportunity across various market segments.
Market Key Highlights
________________________________________________________________
Frozen Vegetables Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
The market expansion is fundamentally propelled by the nexus of changing demographics, verifiable nutritional science, and advancements in convenience packaging. The key driver is the globally increasing urbanization and resulting time constraint on working populations. This imperative directly elevates the demand for frozen vegetables by positioning them as a fast, pre-cleaned, and pre-cut ingredient that drastically reduces meal preparation time. The perception of frozen products has benefited significantly from scientific comparisons confirming that vegetables quick-frozen at their peak ripeness retain comparable, and often higher, levels of key nutrients like Vitamin C and B vitamins compared to fresh produce that has been subjected to lengthy storage and transport. This scientific validation acts as a powerful catalyst, overcoming historical consumer skepticism and shifting demand from the perceived 'freshness' of chilled products to the proven nutritional consistency of frozen alternatives. Furthermore, the rising awareness of food waste motivates environmentally conscious consumers to purchase frozen vegetables, which offer a significantly longer storage period, mitigating spoilage and driving demand through a sustainability-focused value proposition.
Challenges and Opportunities
The market faces persistent headwinds related to energy intensity and raw material price volatility. The frozen vegetable supply chain is inherently energy-intensive, from initial quick-freezing and cold storage to refrigerated transport. Fluctuations in global energy markets translate directly into higher operating and logistical costs, which can constrain the manufacturer's ability to maintain competitive retail pricing, thereby posing a downward pressure on price-sensitive consumer demand.
Conversely, the dominant opportunity lies in the burgeoning global demand for organic, non-GMO, and "clean label" products. This trend is a clear demand driver, as consumers are increasingly scrutinizing ingredient lists. Leading companies have responded by publicly committing to removing artificial colors and minimizing chemical additives in their frozen vegetable lines, directly appealing to health-conscious retail buyers. This focus on premium, minimally processed offerings creates a strong differentiation strategy that supports higher average selling prices and drives segment growth, particularly in North America and Europe.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The Frozen Vegetables Market is a physical product market, making the raw material and pricing analysis a critical component of supply chain stability. The primary raw materials are fresh, field-grown vegetables, which represent an agricultural commodity market. Pricing dynamics are therefore acutely exposed to seasonal yield variability, weather patterns, and regional agricultural policy. A supply-side shock, such as a major drought or unexpected cold snap in a key production region, instantly constricts the available volume of a specific vegetable (e.g., peas, corn) suitable for processing. This supply constriction necessitates a corresponding price increase for processors, which, through cost-plus pricing models, is transferred to the retail price of the final frozen product. The overall long-term pricing trend reflects an increasing cost pressure driven by rising labor wages in agricultural hubs and elevated costs for energy and fertilizers. This dynamic compels processors to optimize input purchasing and invest in advanced harvesting technology to mitigate raw material price risk and stabilize consumer-facing prices to maintain demand elasticity.
Supply Chain Analysis
The global frozen vegetable supply chain is a cold-chain-dependent matrix defined by rapid processing and complex logistics. The chain begins with specialized agricultural production focused on high-yield cultivars suitable for mechanical harvesting and freezing. The key production hubs are concentrated in regions with large-scale, mechanized agriculture, primarily Western Europe (e.g., Belgium, France), North America (e.g., the Pacific Northwest), and major exporting nations like China. The critical logistical complexity is the mandate for speed, as vegetables must be harvested, blanched (for enzymatic deactivation), and quick-frozen within hours to lock in nutrients and texture. This mandates direct co-location of processing facilities near farming operations. The market's dependency is acutely tied to the quality and reliability of refrigerated transport (reefers) and cold storage warehousing, especially for intercontinental trade. Any failure in temperature maintenance, known as a cold chain break, can render the entire batch unsaleable, significantly increasing logistical risk and impacting the overall supply-side reliability, which can cause intermittent supply gaps in retail demand.
Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| European Union (EU) | Council Directive 89/108/EEC on quick-frozen foodstuffs (Temperature Monitoring) | Increases demand confidence. This Directive mandates that quick-frozen food be held at -18°C or lower, with a maximum deviation of 3°C during transport and distribution. This strict temperature control ensures verifiable quality and nutrient preservation, serving as a non-tariff barrier that elevates consumer trust in product safety and quality, thereby sustaining demand. |
| India | Food Safety and Standards (Import) Regulations, 2017 / FSSAI | Regulates and controls import demand. The FSSAI mandates rigorous inspection, sampling, and clearance procedures for all imported frozen food consignments. This stringent oversight, including the requirement for an import license, protects domestic producers while assuring consumers of import quality, structuring the competitive dynamics between domestic and international supply. |
| United States | FDA Food Code & USDA Regulations (Labeling and Standards of Identity) | Shapes consumer choice and demand transparency. The USDA and FDA jointly set standards for product identity (e.g., what constitutes a vegetable blend) and mandatory labeling requirements. The recent industry focus on the voluntary removal of FD&C colors, driven by consumer pressure, is a direct market response to the transparency framework enforced by these agencies, directly increasing demand for reformulated, "cleaner" products. |
________________________________________________________________
In-Depth Segment Analysis
By Product Type: Cruciferous Vegetables
The Cruciferous Vegetables segment, encompassing products like frozen broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts, has demonstrated a significant demand surge, largely driven by the popularity of high-protein and low-carbohydrate dietary trends. The segment's demand is principally catalyzed by the keto and paleo movements, which promote the consumption of vegetables as a low-starch, nutrient-dense substitute for grain-based foods. Specifically, frozen cauliflower has become a versatile demand proxy for starches like rice and potatoes, driven by extensive product development in the retail sector—including cauliflower rice, pizza crusts, and mash. This segment benefits from its inherent convenience for this substitution: the quick-frozen form maintains structural integrity better than fresh when cooked as a starch alternative, making it the preferred format for recipe adherence and time-saving preparation. This specific, function-driven demand validates cruciferous vegetables as a high-growth category distinct from generic frozen vegetable mixes.
By End-User: Retail Consumers
The demand dynamics from Retail Consumers are primarily centered on the dual factors of affordability and sustained convenience in an inflationary environment. For the average household, frozen vegetables serve as a crucial component of cost management, offering a year-round, price-stable alternative to volatile fresh produce prices. The extended shelf life of frozen products directly addresses a core retail consumer imperative: mitigating household food waste, which provides a tangible financial benefit. Furthermore, the retail sector's demand is directly amplified by the industry's strategic focus on value-added, pre-portioned, and pre-seasoned vegetable sides. This shift in product offering caters to the increasing number of consumers who value time savings and meal simplicity over scratch-cooking, effectively embedding frozen vegetables as an essential, high-utility staple in the modern grocery cart, ensuring a consistent volume pull through the retail channel.
________________________________________________________________
Geographical Analysis
- US Market Analysis (North America): The US market for frozen vegetables is dominated by a mature cold chain infrastructure and a powerful consumer trend toward health-driven convenience. Local demand is specifically shaped by the widespread adoption of single-serving, brand-differentiated frozen meals and side dishes. Major manufacturers focus on introducing high-protein, organic, and ethnically-inspired frozen vegetable blends to cater to a diverse and affluent consumer base.
- Brazil Market Analysis (South America): Brazil represents a market with growing demand driven by rapid urbanization and expanding middle-class disposable income. The local factor impacting demand is the rising penetration of organized retail and the gradual improvement of the cold chain infrastructure outside of major metropolitan areas.
- Germany Market Analysis (Europe): Germany's frozen vegetable market is highly structured and characterized by stringent quality expectations and a strong preference for organic and regional sourcing. Local demand is fundamentally supported by the EU's strict quick-freezing regulations, which reinforce a high level of consumer trust in product quality.
- Saudi Arabia Market Analysis (Middle East & Africa): The Saudi Arabian market's demand for frozen vegetables is primarily shaped by climatic limitations on local fresh produce and reliance on global trade. The severe climate makes high-quality, year-round fresh vegetable supply logistically complex and expensive.
- China Market Analysis (Asia-Pacific): China is characterized by a dual-market structure: a dominant export-oriented processing industry and a rapidly emerging domestic consumption market. Local demand is being spurred by rising food safety consciousness and the proliferation of e-commerce and cold-chain logistics in tier-one and tier-two cities.
________________________________________________________________
Competitive Environment and Analysis
The competitive landscape of the frozen vegetables market is an intricate structure dominated by global, diversified food conglomerates and supported by a strong foundation of regional, specialized processors. Competition revolves around brand equity, cold chain mastery, and rapid product innovation in high-growth segments like organic and plant-based foods. Major players leverage their deep retail relationships and robust distribution networks to maintain shelf-space dominance.
The key companies identified in the market include General Mills Inc., Conagra Brands, and Bonduelle Group.
- Conagra Brands (Birds Eye, Healthy Choice, Marie Callender's): Conagra Brands, a North American powerhouse in branded foods, strategically anchors its frozen vegetable dominance through its portfolio, most notably the Birds Eye brand. The company's strategic positioning centers on market leadership in product innovation and portfolio modernization.
- Bonduelle Group: The Bonduelle Group, headquartered in France, maintains a competitive position through its European expertise in agricultural procurement and processing efficiency across both canned and frozen vegetables. The group's strategy emphasizes its B Corp certification journey and its commitment to a plant-rich diet transition.
- General Mills Inc. (Green Giant): General Mills Inc. focuses its frozen vegetable strategy through its prominent brand, Green Giant. Although the company's recent strategic focus has been portfolio management and efficiency, its competitive strength remains in its unparalleled brand recognition and deep distribution penetration within North American retail channels.
________________________________________________________________
Recent Market Developments
- June 2025: Conagra Brands Launches Over 50 New Frozen Food Items Conagra Brands, Inc. announced the debut of more than 50 new frozen food products across its brand portfolio, including new single-serve and multi-serve meals, and various vegetable side dishes.
- June 2025: Conagra Brands Announces FD&C Color Removal Milestone Conagra Brands, Inc. announced its plan to complete the removal of certified Food, Drug & Cosmetic colors ("FD&C colors") from its entire U.S. frozen product portfolio by the end of 2025.
________________________________________________________________
Frozen Vegetables Market Segmentation
- By Product Type
- Leafy Vegetables
- Root Vegetables
- Cruciferous Vegetables
- Others
- By Distribution Channel
- Online
- Offline
- Supermarkets & Hypermarkets
- Convenience Stores
- By End-User
- Retail Consumers
- Food Services
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- South America
- Europe
- Middle East and Africa
- Asia Pacific
Frozen Vegetables Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Frozen Vegetable Market Size in 2025 | US$19.23 billion |
| Frozen Vegetable Market Size in 2030 | US$23.41 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 4.01% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Frozen Vegetable Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |