Report Overview
Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market Highlights
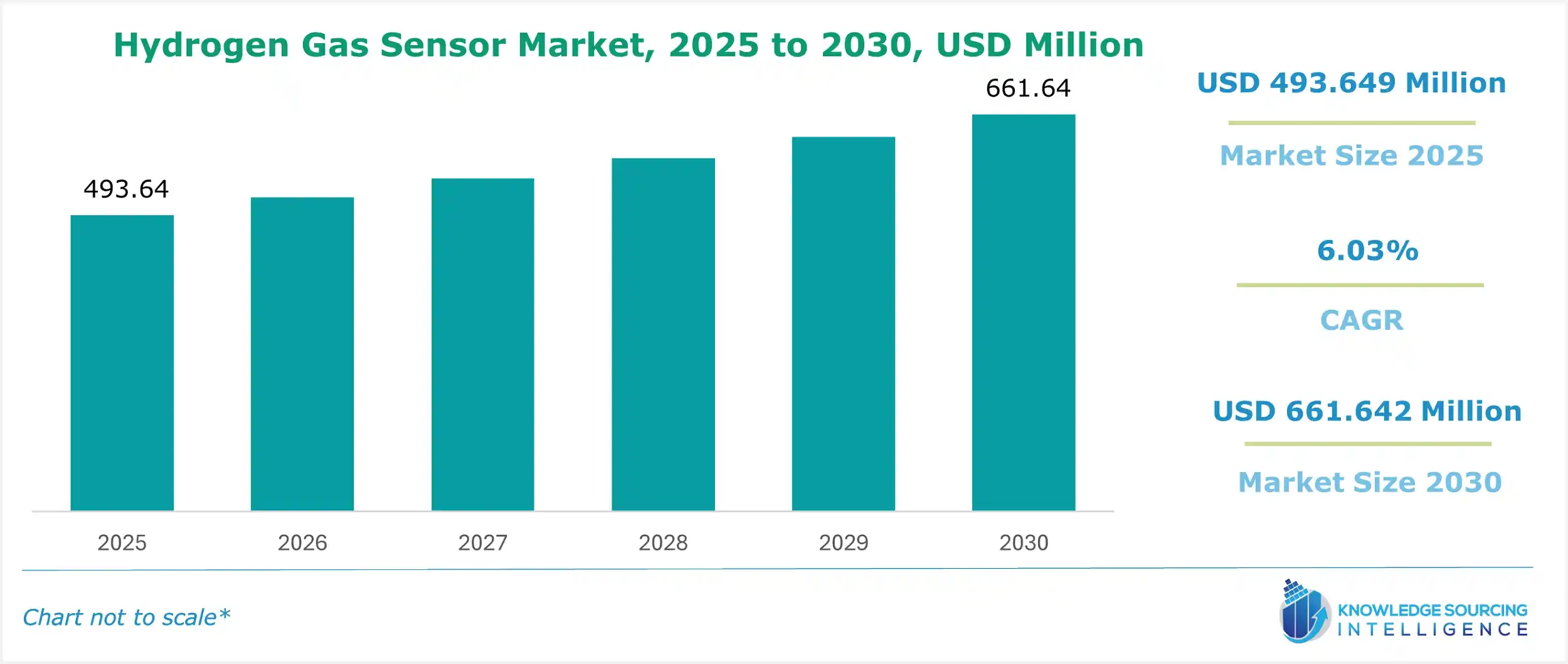
Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market Size:
The global hydrogen gas sensor market is evaluated at US$493.649 million in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.03%, reaching US$661.642 million by 2030.
The demand for hydrogen as an alternative to traditional fuel has been rising recently. As this transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable source of energy increases, the demand for hydrogen sensors will increase. These sensors ensure that safe storage, handling, and usage are done properly and that no leaks are registered in various end-user industries.
Further, various research organizations are investing in hydrogen gas as it is a cleaner and safer option. For instance, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre launched a hydrogen gas sensor (model: TDP-BARC H2-054P). This is a catalytic-type detector and can be used for the detection of hydrogen gas ranging from 0.5-4%. This gas sensor has a long lifespan, can be used continuously, is simple to use, and can be easily installed and calibrated.
Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market Growth Drivers:
- Rising shift towards silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) materials
Wide and ultrawide bandgap power electronic semiconductors represent a transformative innovation in the power electronics sector. These state-of-the-art materials outperform traditional Si-based products, including silicon carbide (SiC), gallium nitride (GaN), and diamond. In recent years, substantial improvements have been made in wide bandgap power electronic semiconductors. It encompasses improvements in material quality, device design, and manufacturing techniques. The development of superior SiC and GaN substrates, progress in crystal growth methods, and refinement in device production processes have resulted from collaborative efforts between academic and industry stakeholders. These advancements have made wide bandgap devices increasingly viable commercially. This is driven by heightened material performance, improved device yields, and reduced production costs.
SiC stands out as one of the extensively researched and readily available wide bandgap materials. It possesses a bandgap energy of approximately 3.3 electron volts (eV), a notable increase compared to silicon’s 1.1 eV. Power devices based on SiC offer multiple advantages, including reduced conduction and switching losses, heightened tolerance to higher temperatures, and enhanced overall efficiency. Another noteworthy wide bandgap material is GaN, which has recently garnered significant attention. GaN exhibits a bandgap energy of approximately 3.4 eV, similar to SiC. Power devices based on GaN demonstrate exceptional performance characteristics, including high breakdown voltages, swift switching speeds, and low on-resistance.
- Increasing environmental concern is also boosting market growth
According to the Global Carbon Budget, carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial and combustion processes are expected to hit 41.6 billion tons in 2024. This is up from 40.6 billion tons in 2023. Governments are opting for hydrogen as a cleaner choice because increased carbon dioxide consumption is contaminating the environment. Over the next few years, commercial applications of hydrogen are expected to create a more pristine environment. Since hydrogen sensors are applicable in the detection of production, storage, distribution, or consumption of hydrogen, their commercial application will enhance their demand and increase market growth.
- Expanding the automotive sector will boost the global hydrogen gas sensor market.
The automotive sector uses hydrogen gas sensors to track and identify hydrogen leaks from fuel cells, enhancing a car's safety performance. Rapid urbanization, technological advancements, and the growing demand for fuel-efficient vehicles have all contributed to the automotive sector's notable boom. According to a 2024 European Automobile Manufacturers' Association (ACEA) report, the number of new car registrations in the EU rose by 0.8%, amounting to approximately 10.6 million units.
Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market Restraints:
- High investment costs may hamper the overall market.
The manufacturing and installation costs are hindering the extensive application of hydrogen gas sensors. Due to the high production costs, quality sensors with precise detection may not be extensively used in applications or industries where cost is a key factor. Moreover, some hydrogen gas sensors might be limited by sensitivity, selectivity, response time, and reliability. If a sensor cannot consistently detect hydrogen at low levels or separate it from other gases, its commercial viability might be compromised.
Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market Geographical Outlook:
- Europe, the Middle East, and Africa are witnessing exponential growth during the forecast period.
The hydrogen gas sensor market is growing in Europe due to the strict regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions and the ambitious hydrogen strategies implemented by countries such as France and Germany. The need for hydrogen as a source of alternative energy has grown due to the European Union's goal to reach carbon neutrality by 2050, which is, in turn, boosting the growth of advanced detection tools faster. The Middle East and African region is also continually expanding owing to its huge production base of hydrogen as well as an ever-growing reliance on clean fuels.
Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market Key Launches:
- In June 2024, the energy technology company Baker Hughes introduced three gas, flow, and moisture measurement sensor technologies intended to boost productivity and safety in hydrogen and other applications in the industrial and energy sectors.
List of Top Hydrogen Gas Sensor Companies:
- Nissha FIS, Inc.
- Membrapor
- Figaro Engineering Inc.
- Aeroqual
- Makel Engineering, Inc.
Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market Size in 2025 | US$493.649 million |
| Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market Size in 2030 | US$661.642 million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 6.03% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Million |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | Americas, Europe, Middle East, and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Hydrogen Gas Sensor Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
The global hydrogen is analyzed into the following segments:
- By Technology
- By End-User Industry
- Automotive
- Oil and Gas
- Healthcare
- Aerospace
- Others
- By Geography
- Americas
- US
- Europe, the Middle East, and Africa
- Germany
- Netherlands
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- Taiwan
- South Korea
- Others
- Americas